Building Information Modeling - Complete Guide
Building Information Modeling (BIM) has transformed our perception of construction and architectural design in the ever-evolving field of contemporary architecture. It is not only a design tool, it is a new paradigm, a digital revolution that extends throughout the whole life cycle of a construction project providing efficiency and accuracy — and a level of planning unimaginable before. Stay with us to discover how BIM enables precision in project planning, reduces errors at the construction stage, and optimizes building performance over the span of its lifecycle. In this article, we discuss the complexities, benefits, use cases, and overall impact that this technology brings to the construction field.
What Is BIM?
Building information modeling (BIM) is one of the most complex digital representations of the physical building. Think of it like a digital twin of a whole building and every part of it can be explored, studied, and analyzed. BIM technology is a key aspect of modern architectural and construction practices because it combines all facets of a construction project. This enables architects, engineers, contractors, building owners, and other stakeholders to work together in this virtual environment. So if the architect improves the design then all the trades can improve and see the changes, implementing the right measures to keep the construction and maintenance efficient.
BIM objects
BIM objects are digital representations of physical building components or materials used in the BIM process. These objects contain detailed information about the product's geometry, appearance, and performance, including but not limited to: windows, door systems, curtain panels, roofing, etc. Using 3D BIM objects allows proper scheduling, planning design, and construction.
Key Features
3D Geometry: each BIM object has a three-dimensional representation that shows its size, shape, and how it fits within a building design.
Data Integration: material type, manufacturer details, performance specifications, installation instructions, and maintenance guidelines.
Parametric Functionality: many objects can adapt to changes in the BIM project, such as resizing or material substitutions, without losing their functionality or data.
Using building information modeling will improve the way the entire construction industry works. BIM helps AEC professionals across industries to exchange information, optimize the lifecycle of a project, and keep the management information up to date.
Benefits of Building Information Modeling
Improved Project Coordination. Building information modeling provides real-time stakeholder interaction. This means that everyone involved in the construction process, from architects to contractors, can work together seamlessly. For example, when an architect makes changes to the design, those alterations are instantly visible to other team members. This level of coordination, combined with clash detection, helps prevent errors and ensures that everyone remains aligned at every stage of the project lifecycle.
Better Visualization. With the use of BIM, you can see the building plan in 3D before construction starts. This helps clients and teams understand the design, verify the information available on file, spot problems early, and make better decisions.
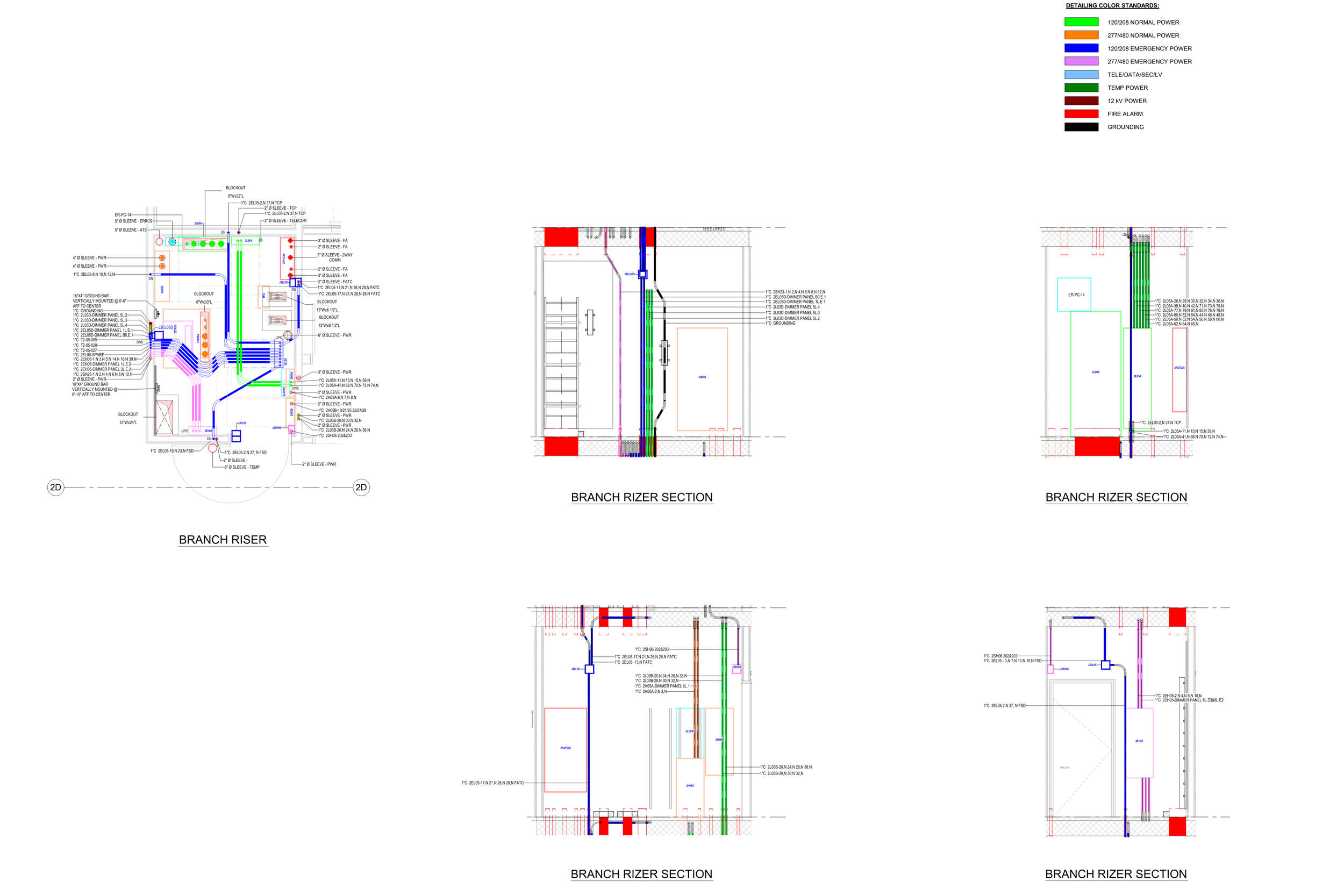
Clash Detection and Risk Mitigation. It is essential in modern construction to coordinate the information and construction drawings in real time, allowing all construction professionals to coordinate in a special software platform designed for clash detection. Unfortunately, the 2D plans can't provide an evenly complex approach to the coordination as 3D BIM and will result in rework and budget leaks. The unified model of the project is a source of information for construction teams, architects, engineers, and other professionals involved in the project. The detail level of bim may differ, but at any level, the base points such as sizes and position should always be included.
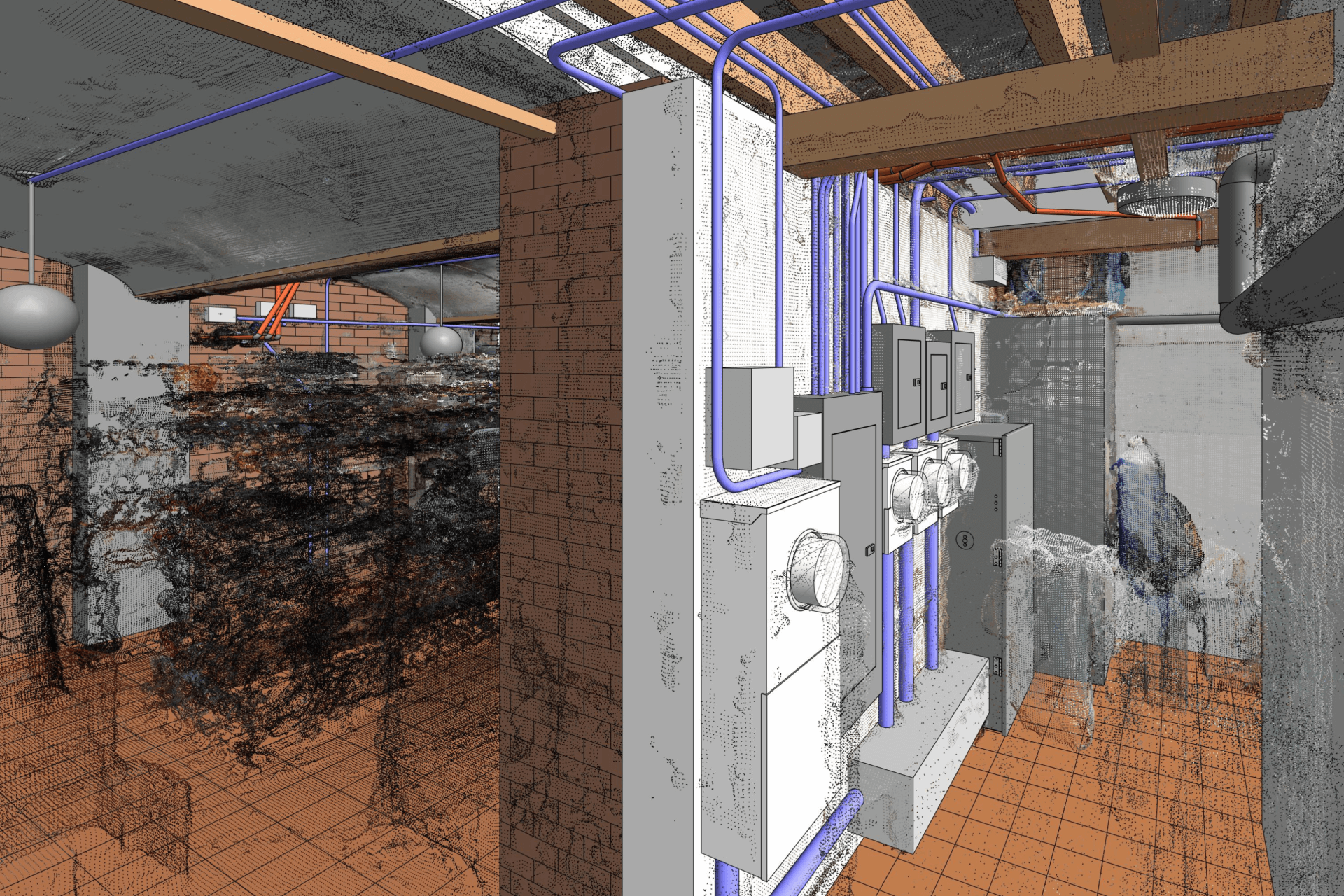
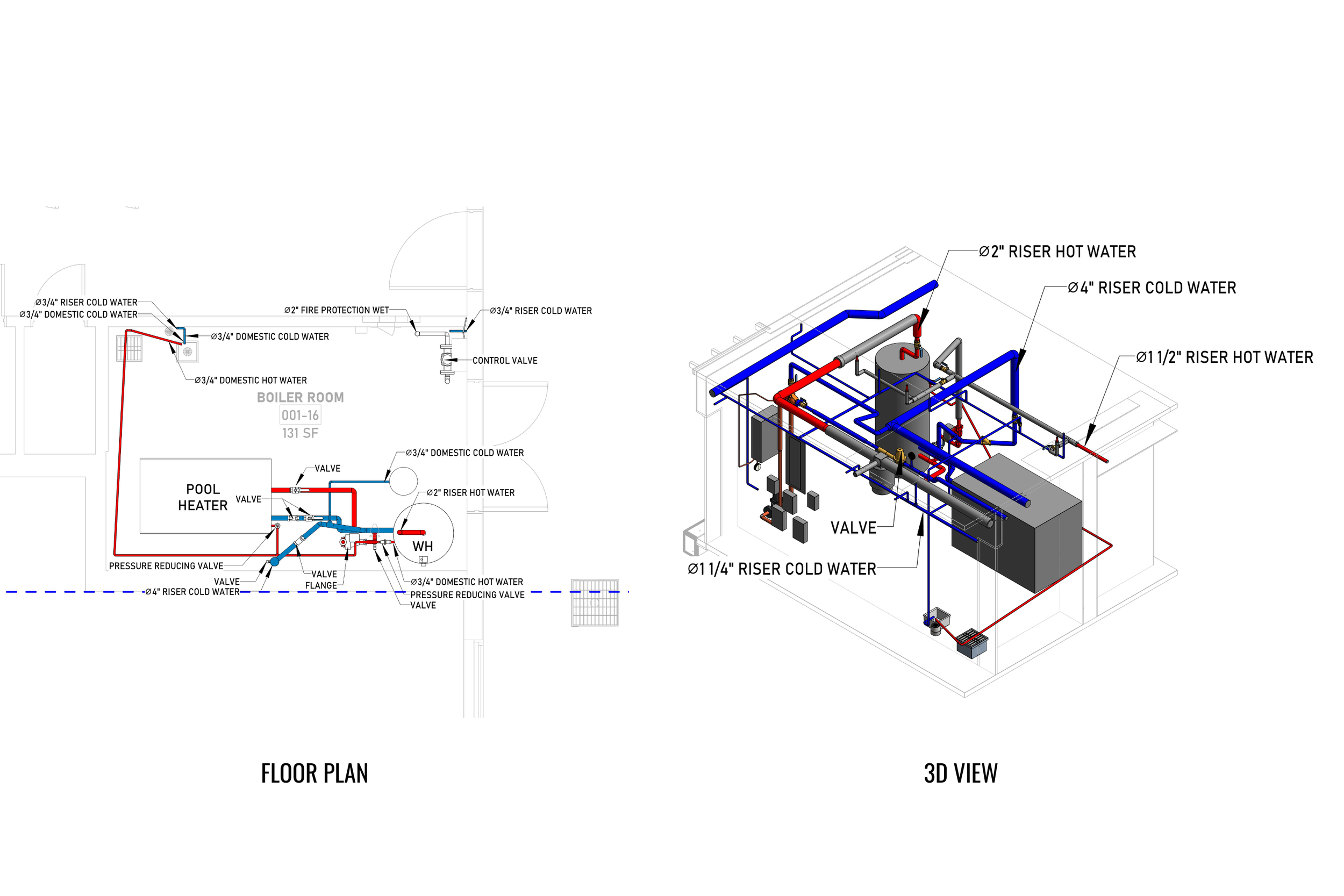
Ensures accurate as-built documentation. BIM facilitates precise as-built documentation, capturing real-world conditions and enabling efficient operation and management. The digital representations capture the true state of the final build, which contains not only structural diagrams but also all systems and components. Using traditional methods that are subject to human error, BIM allows buildings to be detailed in a highly accurate manner and structured documentation. Changes made from design to construction can be tracked effectively using BIM models. If a component of the structure/building is changed or substituted during the construction period, the modification would be updated in the form of BIM. By syncing with changes in the building, this real-time update capability ensures that as-built drawings are always current.
Accurate Cost Estimation. With BIM, you can calculate costs with precision. The model tracks materials, labor, and scheduling data, giving a clear picture of the budget. This accuracy helps reduce costs by minimizing financial surprises and ensuring resources are allocated effectively. The 4D bim is used for proper scheduling of the elements, such as windows, doors, pipes, you name it, also used in prefabrication and modular construction. The BIM data available in schedules helps budget planning, avoid unnecessary ordering, and manage waste.
Key components of BIM
The key components of Building Information Modeling encompass various elements that contribute to the creation, management, and utilization of digital information throughout the lifecycle of a building project.
1. 3D Models
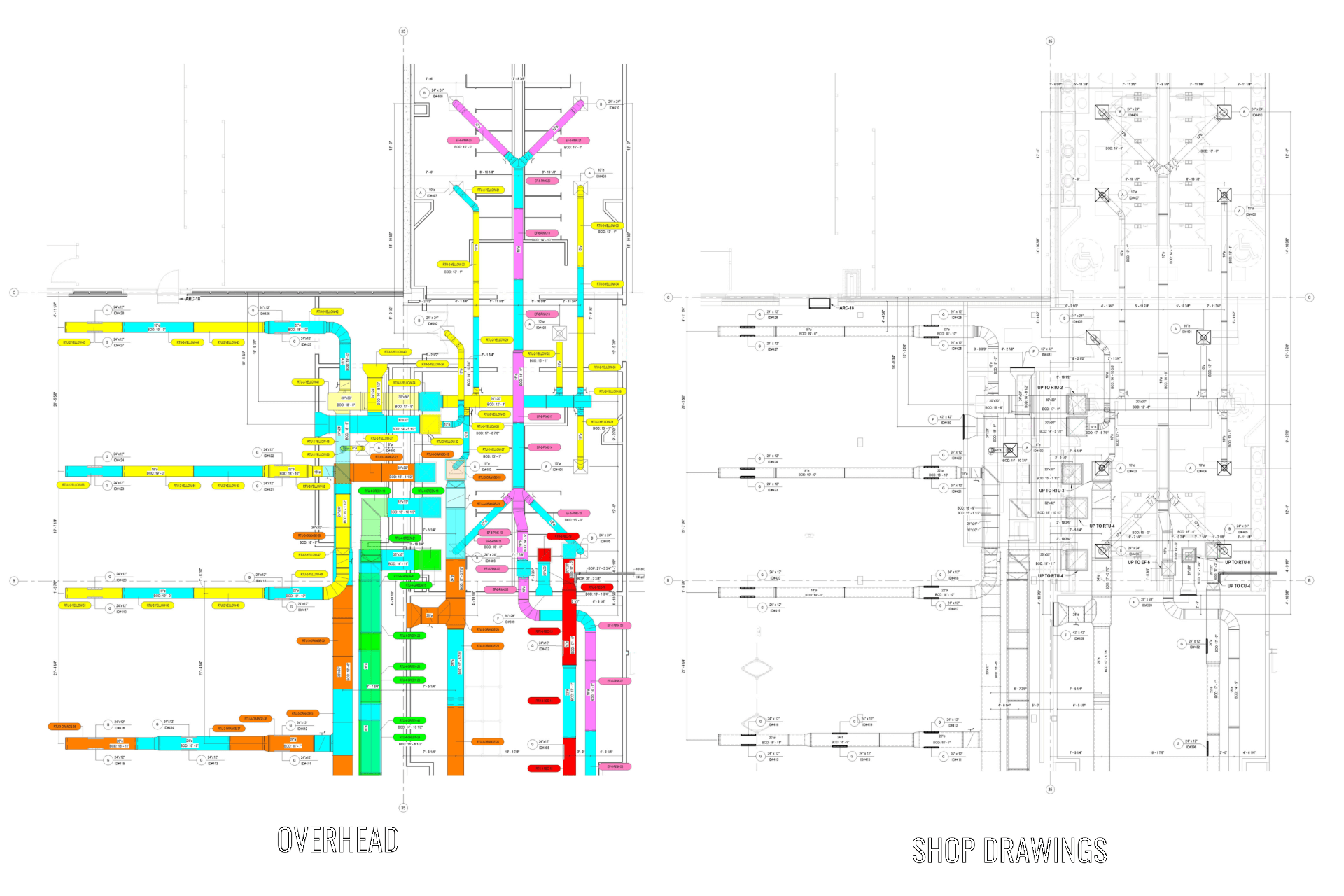
3D models form the foundation of BIM. These digital representations of physical and functional characteristics provide a visual understanding of the building or infrastructure. If the project has been started in 2D, it is recommended to undergo the 2D to 3D phase to ensure the alignment of all the elements, also called PDF-to-BIM.
2. Parametric Design
Parametric design allows the creation of intelligent 3D models where elements are defined by parameters and relationships. Changes to one element can automatically update related elements, enhancing flexibility in design. For example, if you decide to replace one type of window with another type, you don’t have to apply changes to each window individually, by modifying the type all the components will be replaced in a matter of seconds.
3. Data and Information
BIM incorporates extensive data and information associated with model elements. This includes specifications, material properties, cost data, maintenance schedules, and other relevant details which can be accessed in the single model, or on blueprints and drawings.
4. Levels of Detail (LOD) or Levels of Development (LOD)
The LOD specifications define the level of detail in a model's geometry and the amount of information associated with each element. These standards ensure consistency and quality across projects. The higher is LOD - the more information will be included in the BIM model.
For example:
LOD 100: Basic massing models with approximate shapes and sizes.
LOD 200: Generic placeholders with rough geometry and dimensions.
LOD 300: Precise geometry that represents actual dimensions and materials.
LOD 400: Fabrication-ready models with complete details for construction.
LOD 500: As-built models capturing real-world, post-construction conditions.
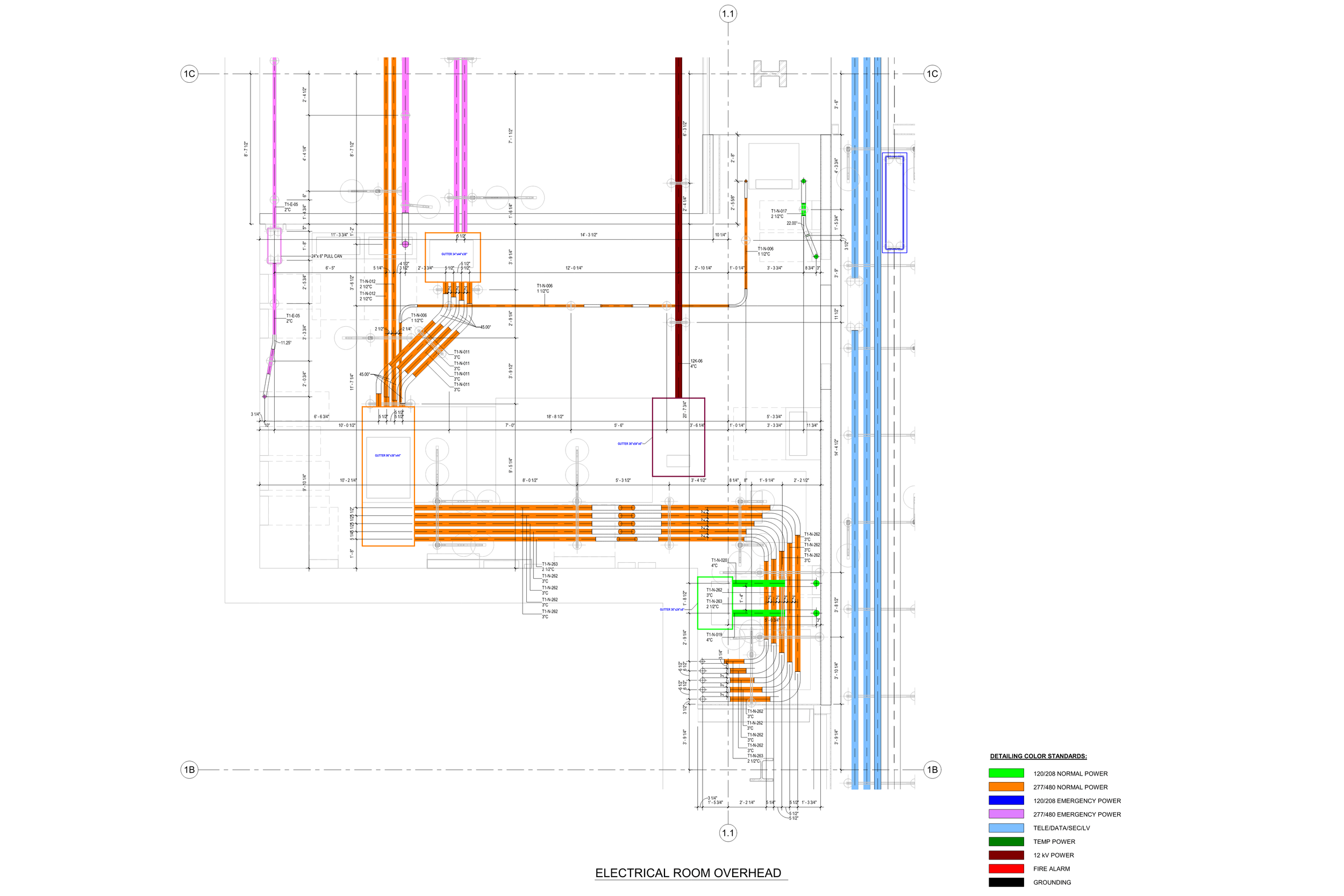
5. Collaboration and Coordination
BIM enables collaborative working among various stakeholders, including architects, engineers, contractors, and facility managers. Coordination tools help identify and resolve clashes or conflicts in the design phase. There are multiple softs and clouds, where creative teams can work simultaneously, and unified models can be used by all the stakeholders simultaneously.
6. BIM Execution Plan (BEP)
An Execution Plan outlines how BIM will be implemented on a specific project. It includes details on project roles, responsibilities, workflows, and information exchange protocols.
7. BIM Analytics and Visualization
Analytics tools analyze data from the model, providing insights into performance, cost estimates, and other key metrics. Visualization tools help communicate complex information to various stakeholders in a comprehensible manner and make informed decisions.
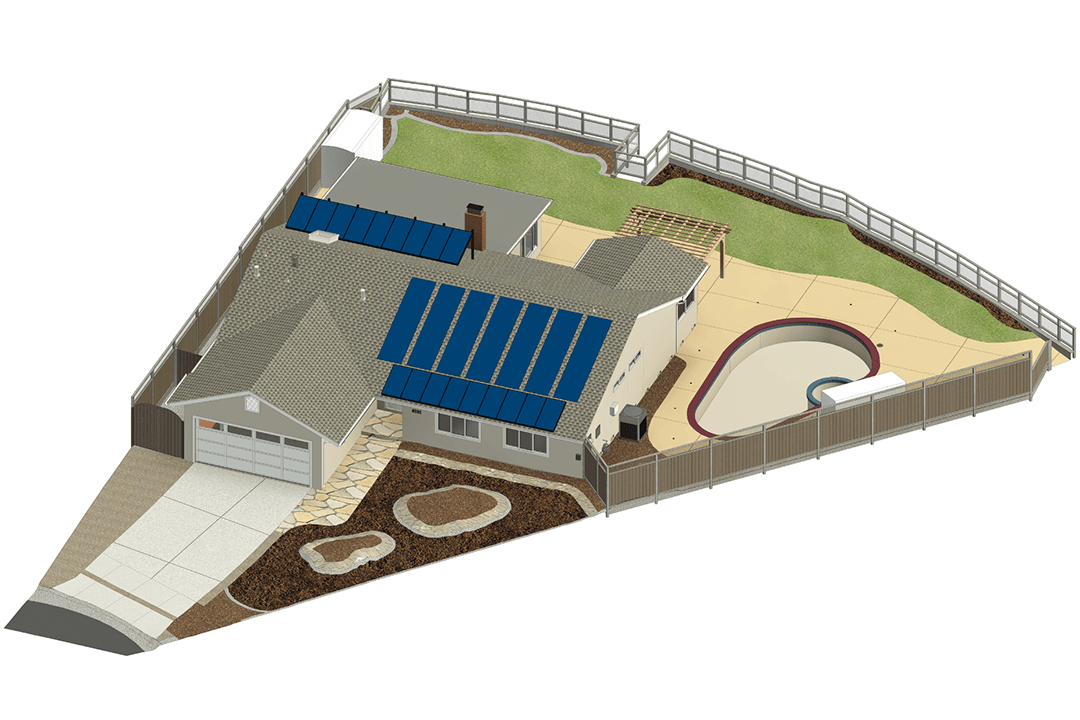
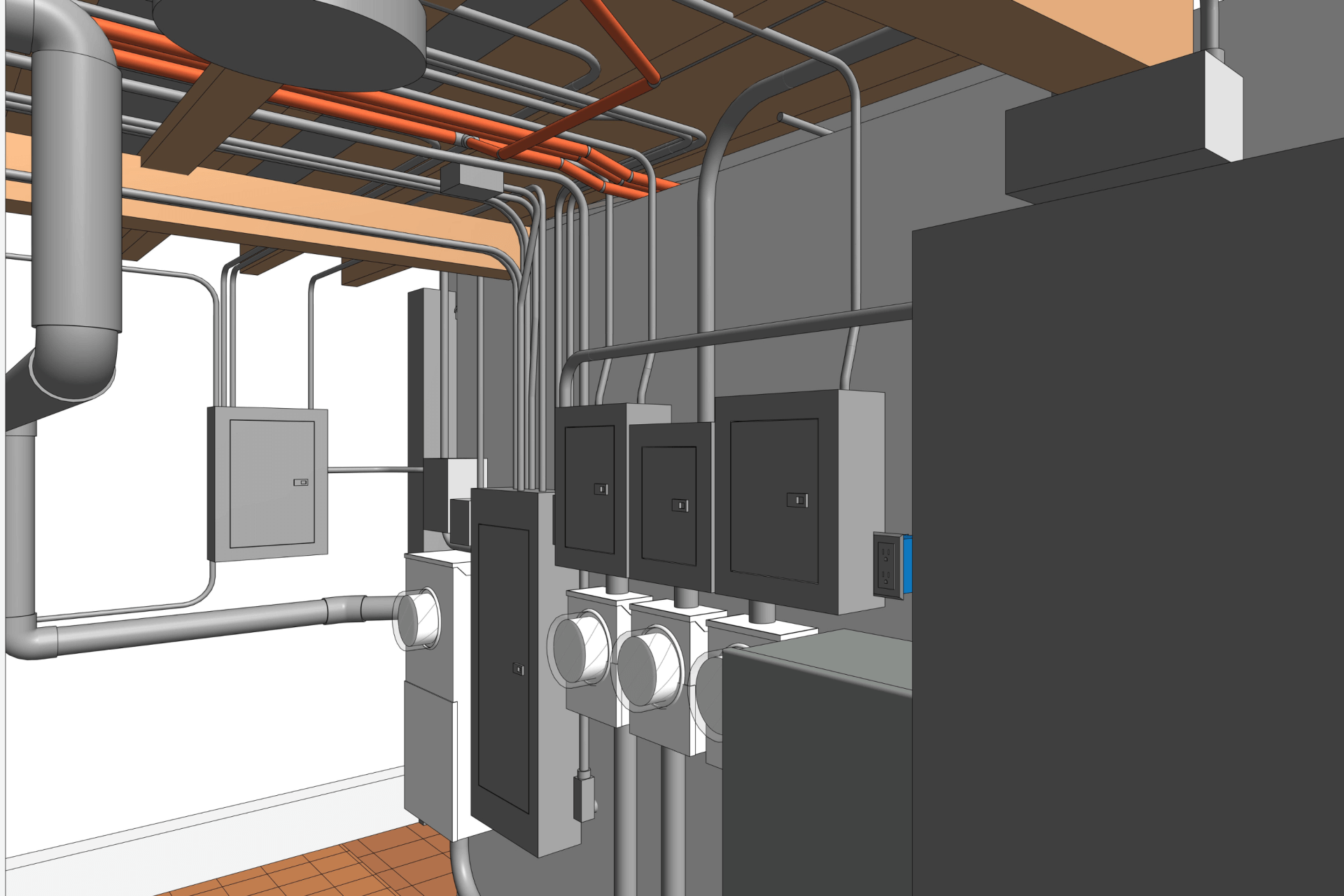
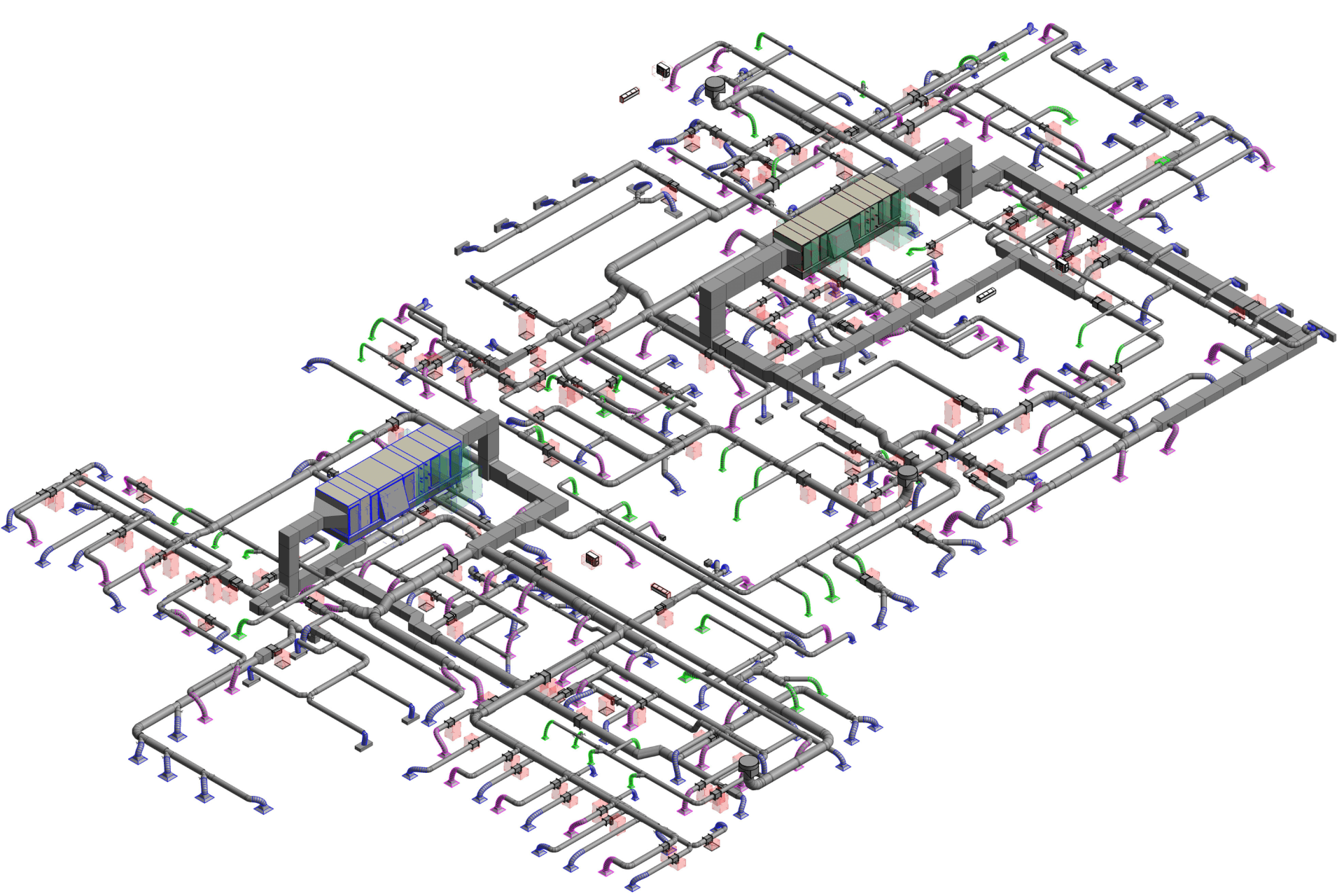
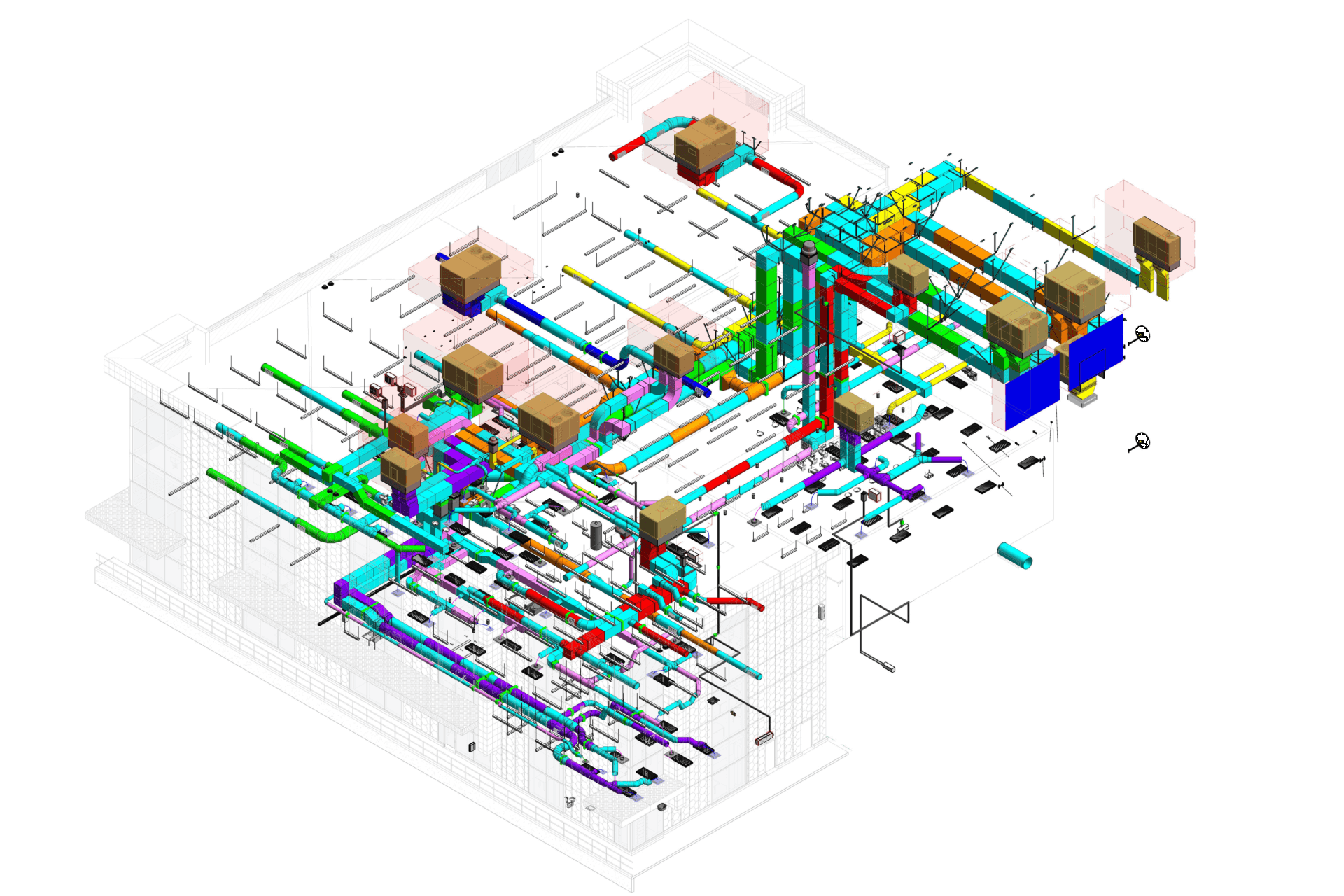
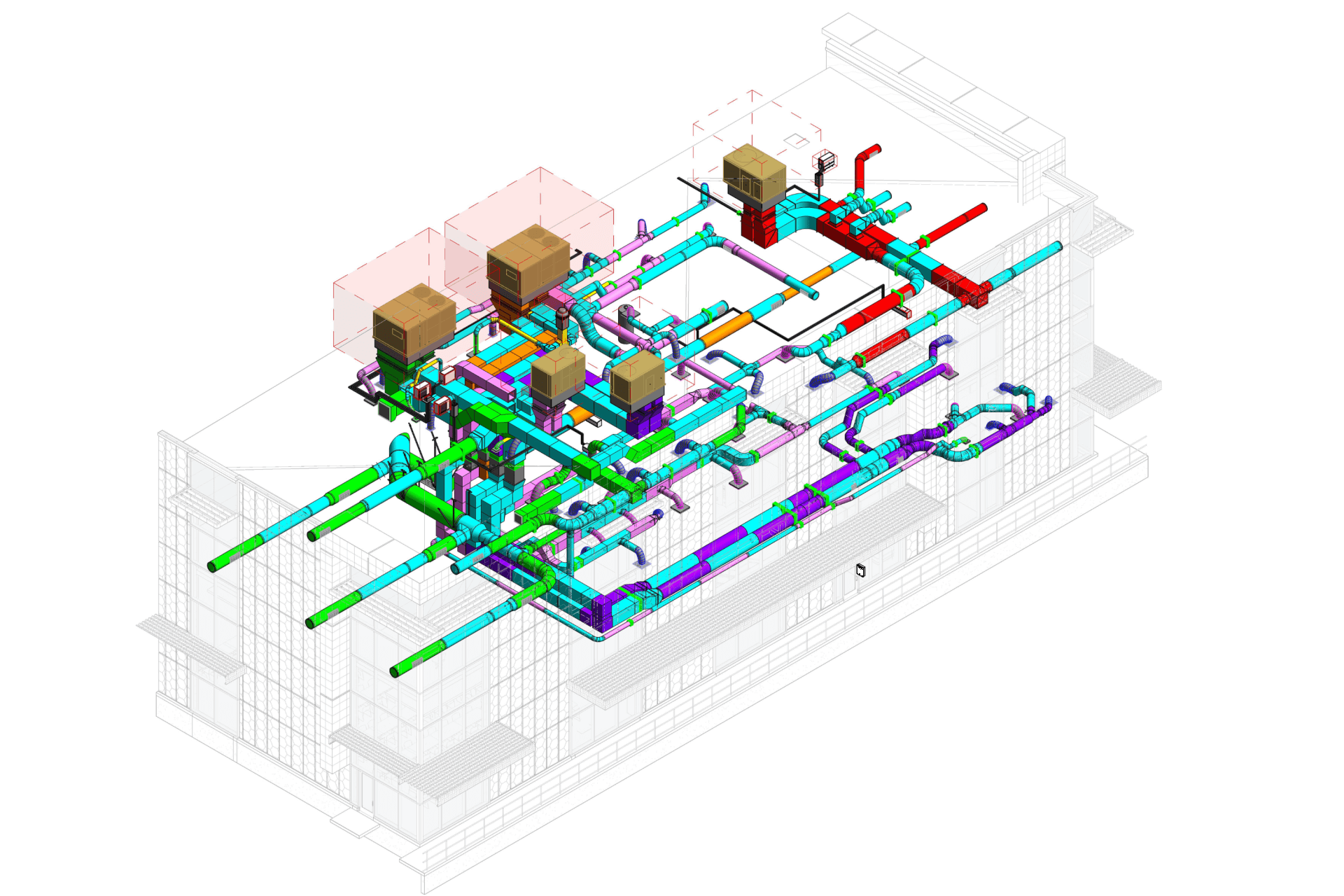
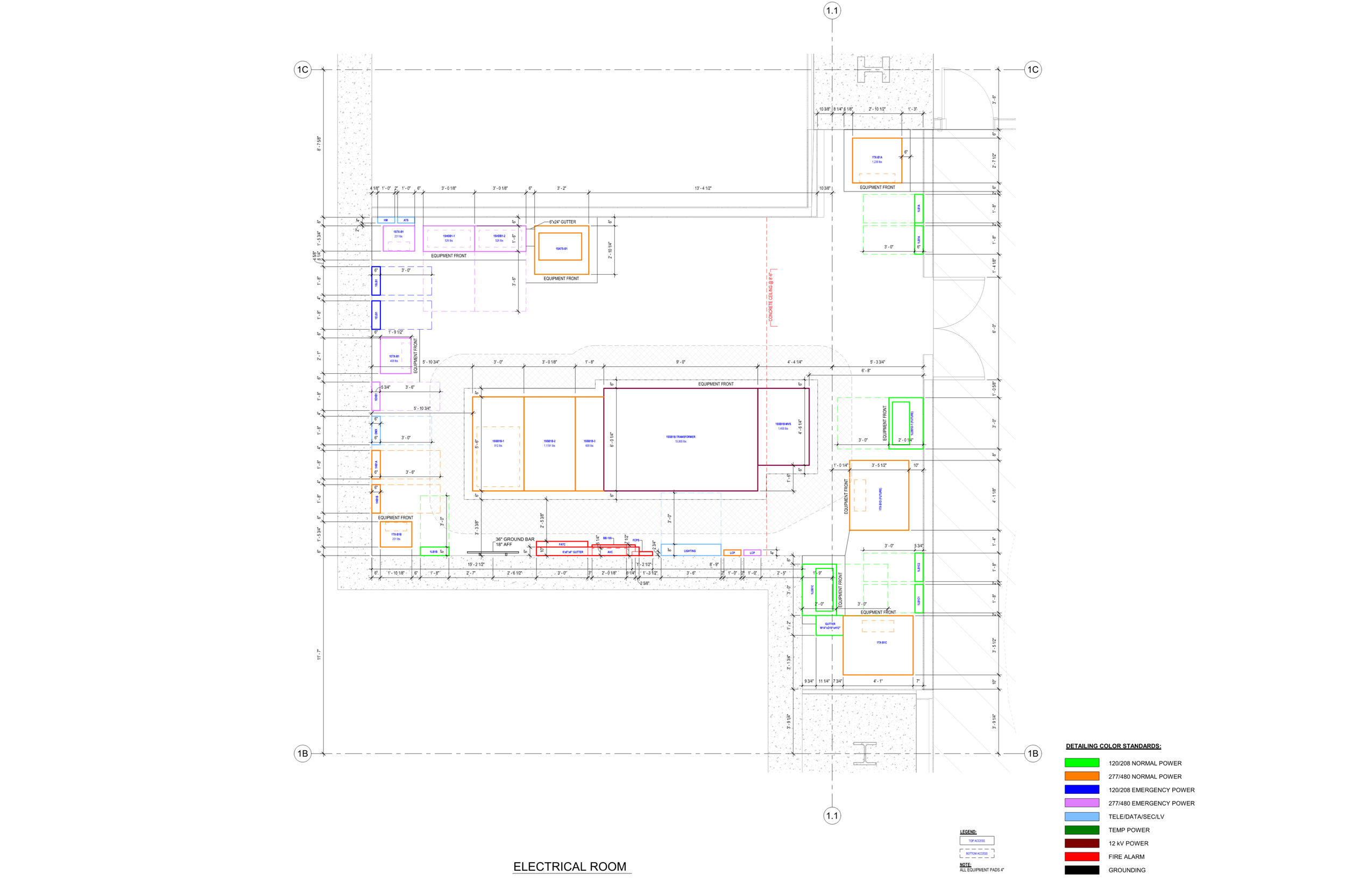
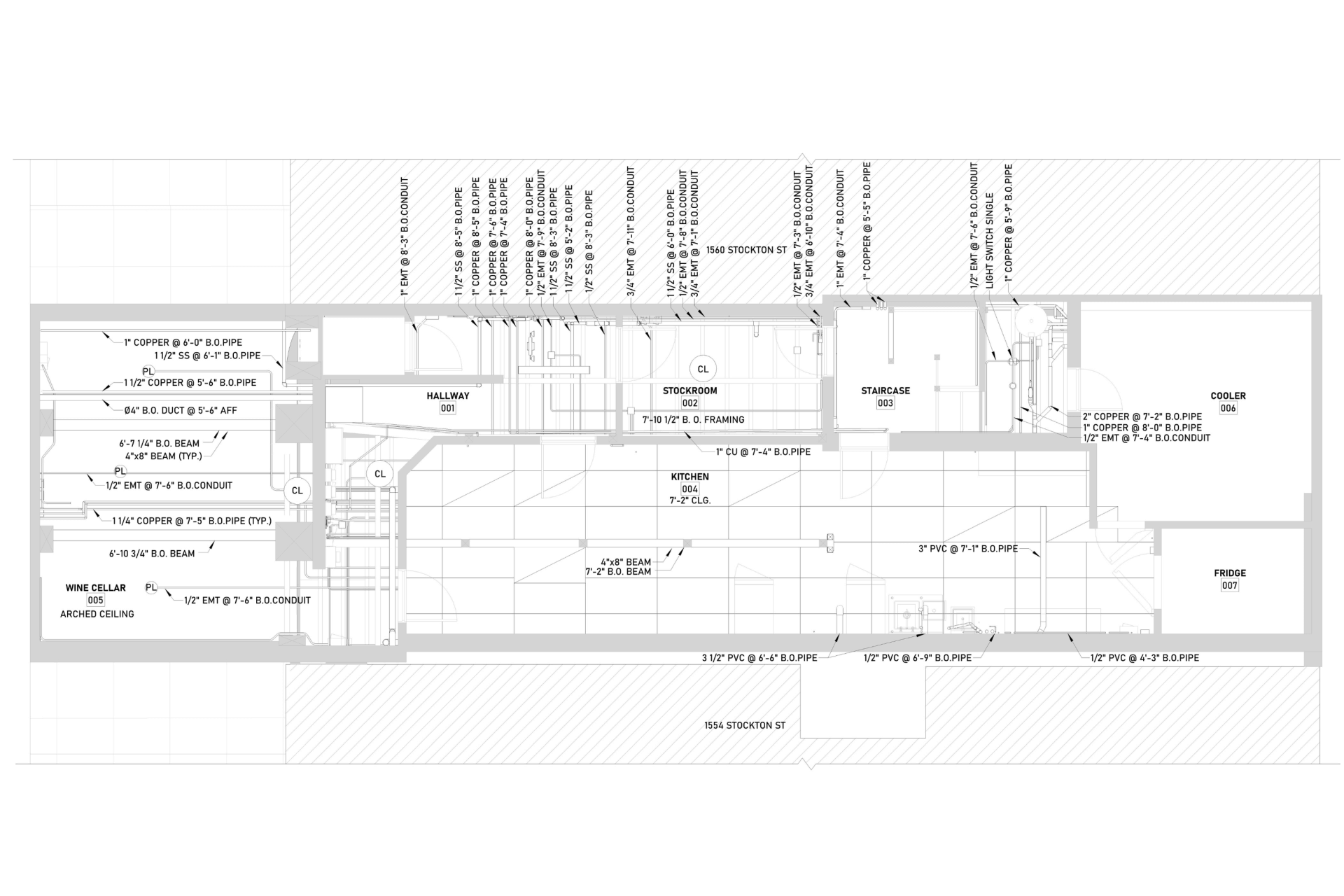
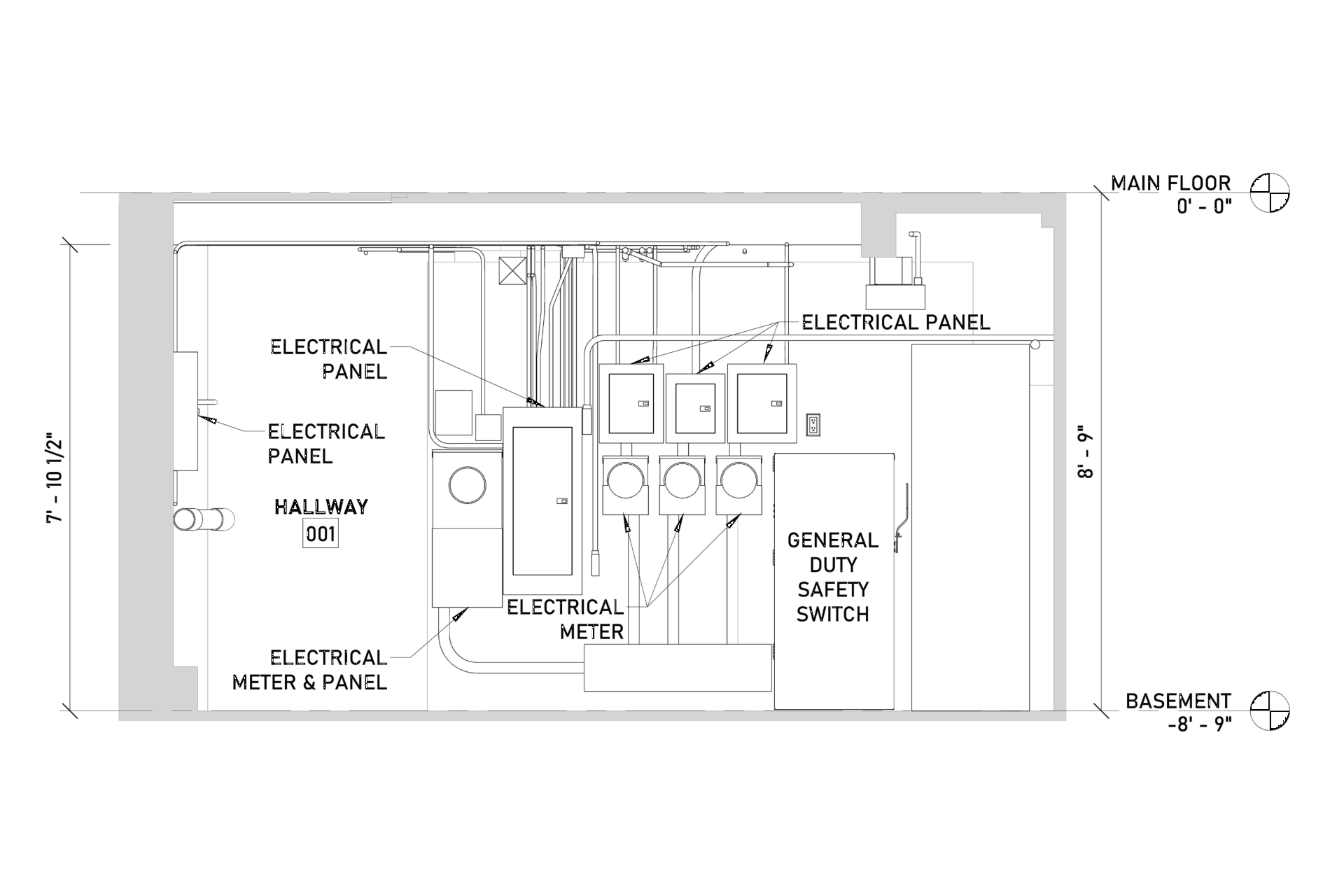
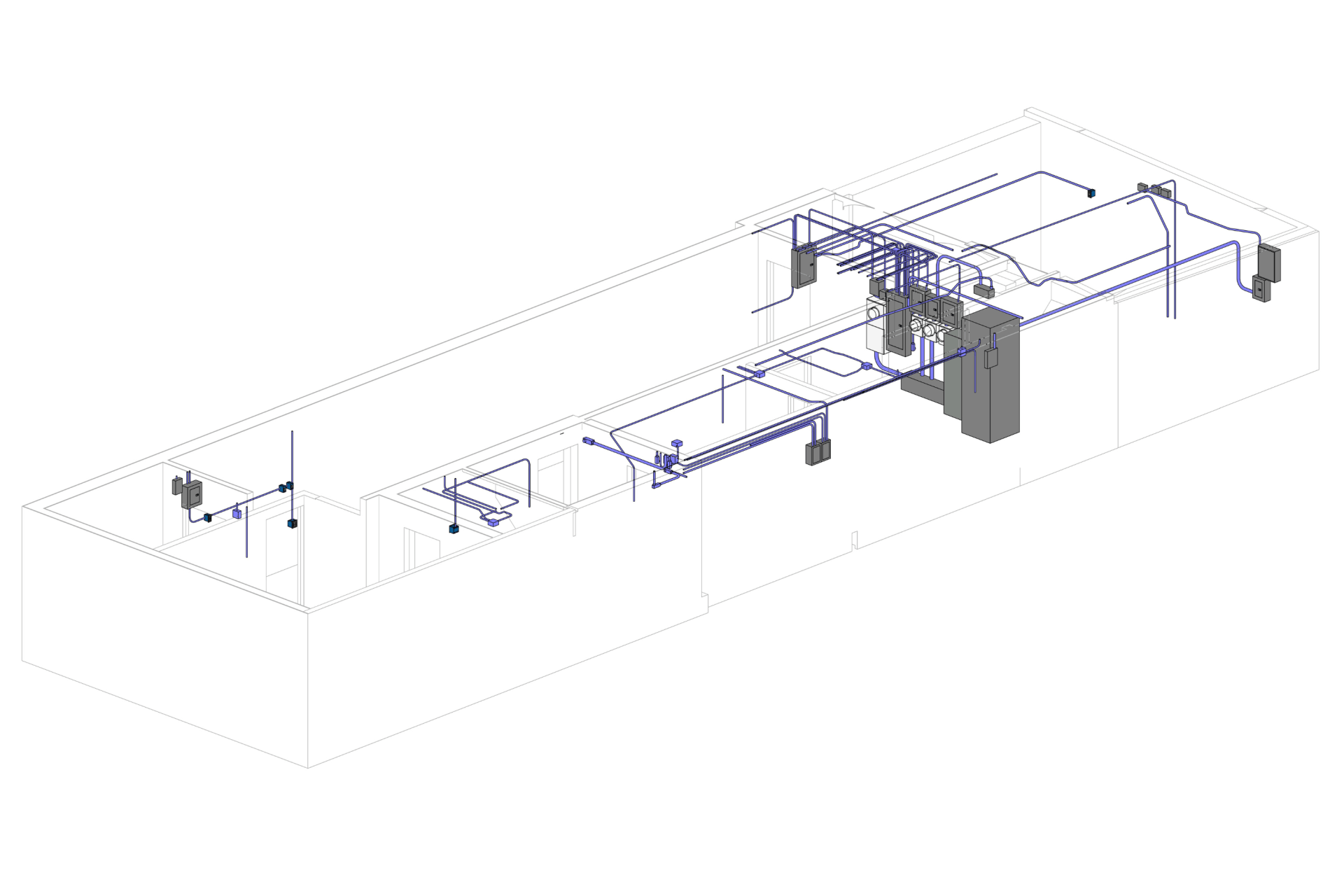
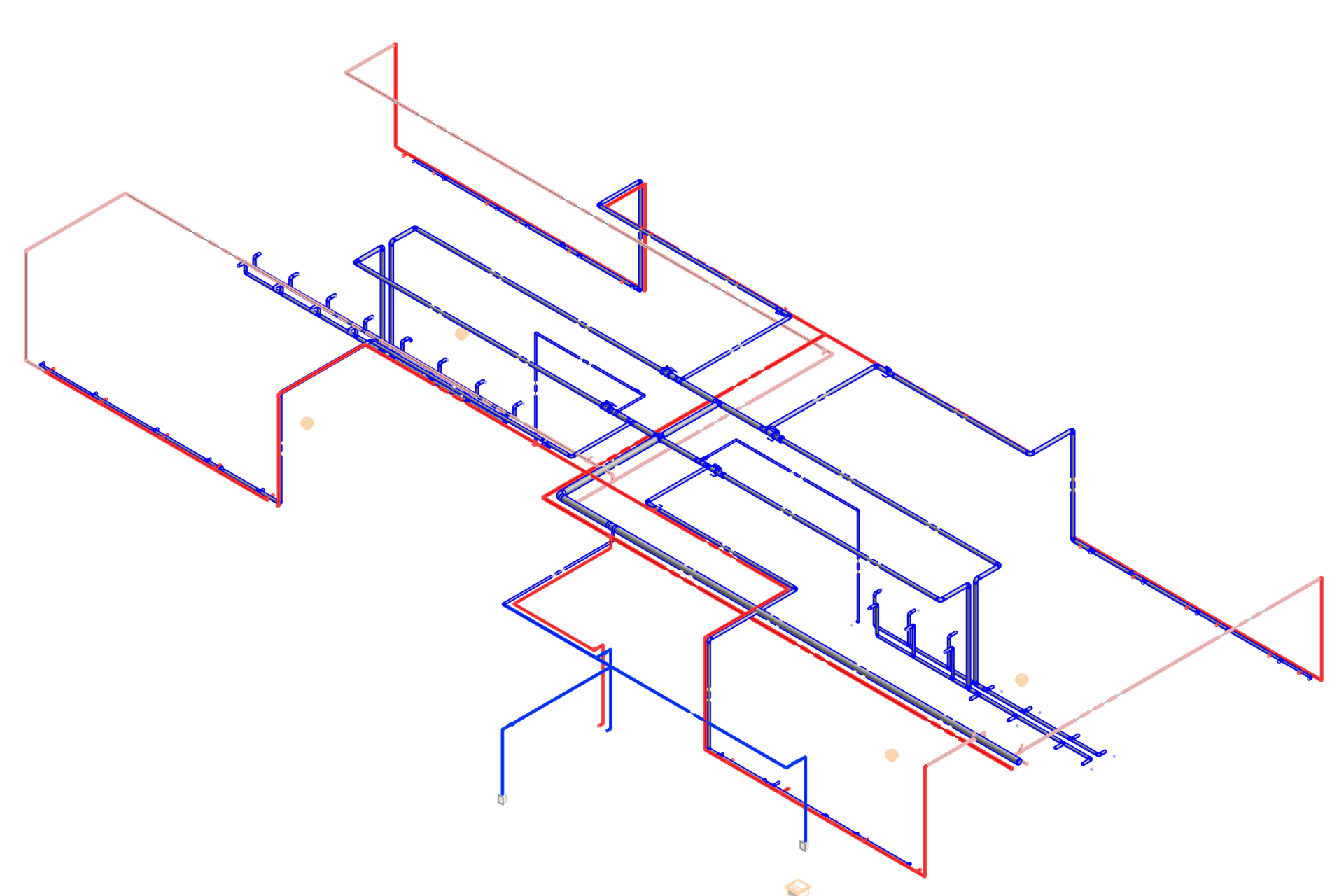
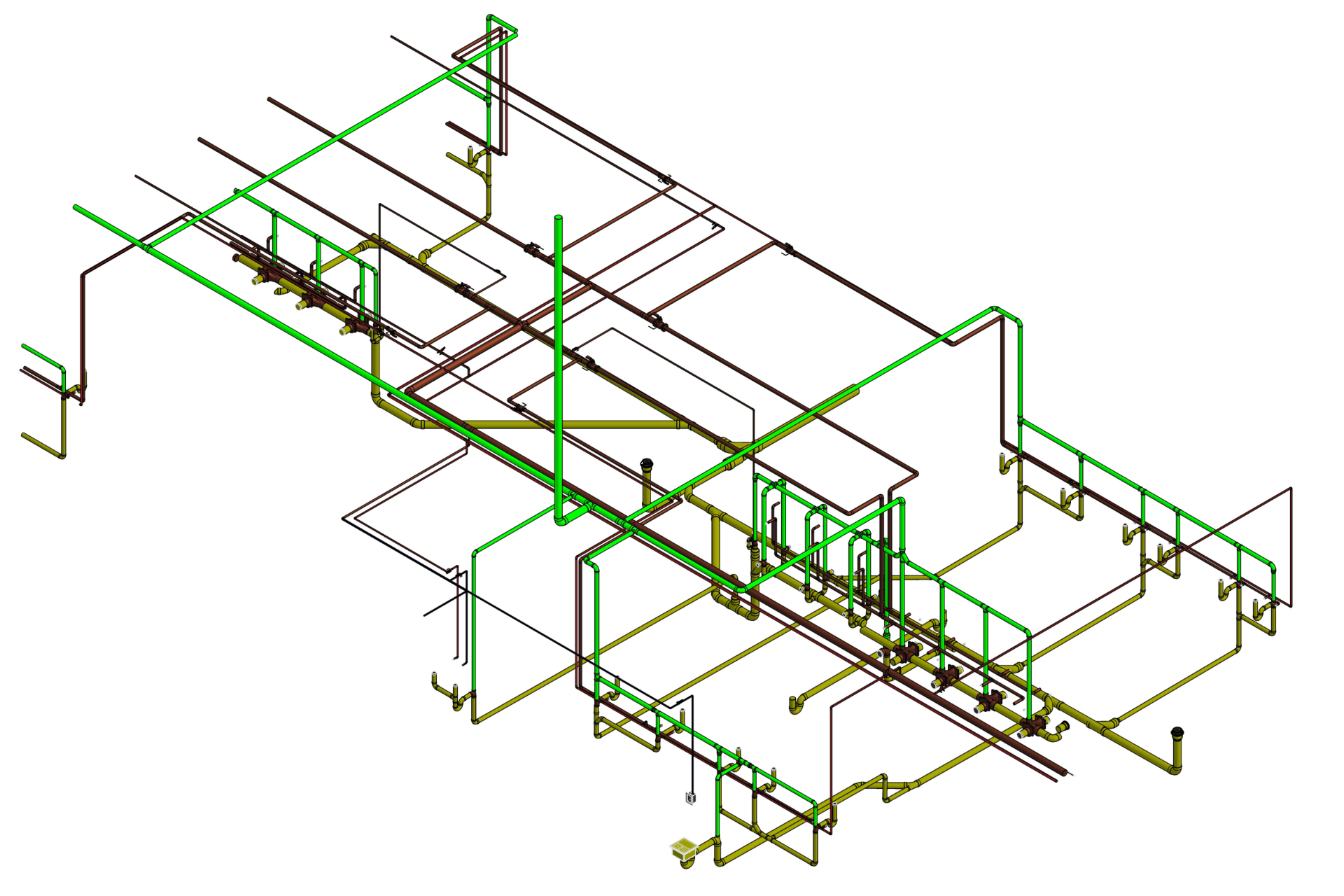
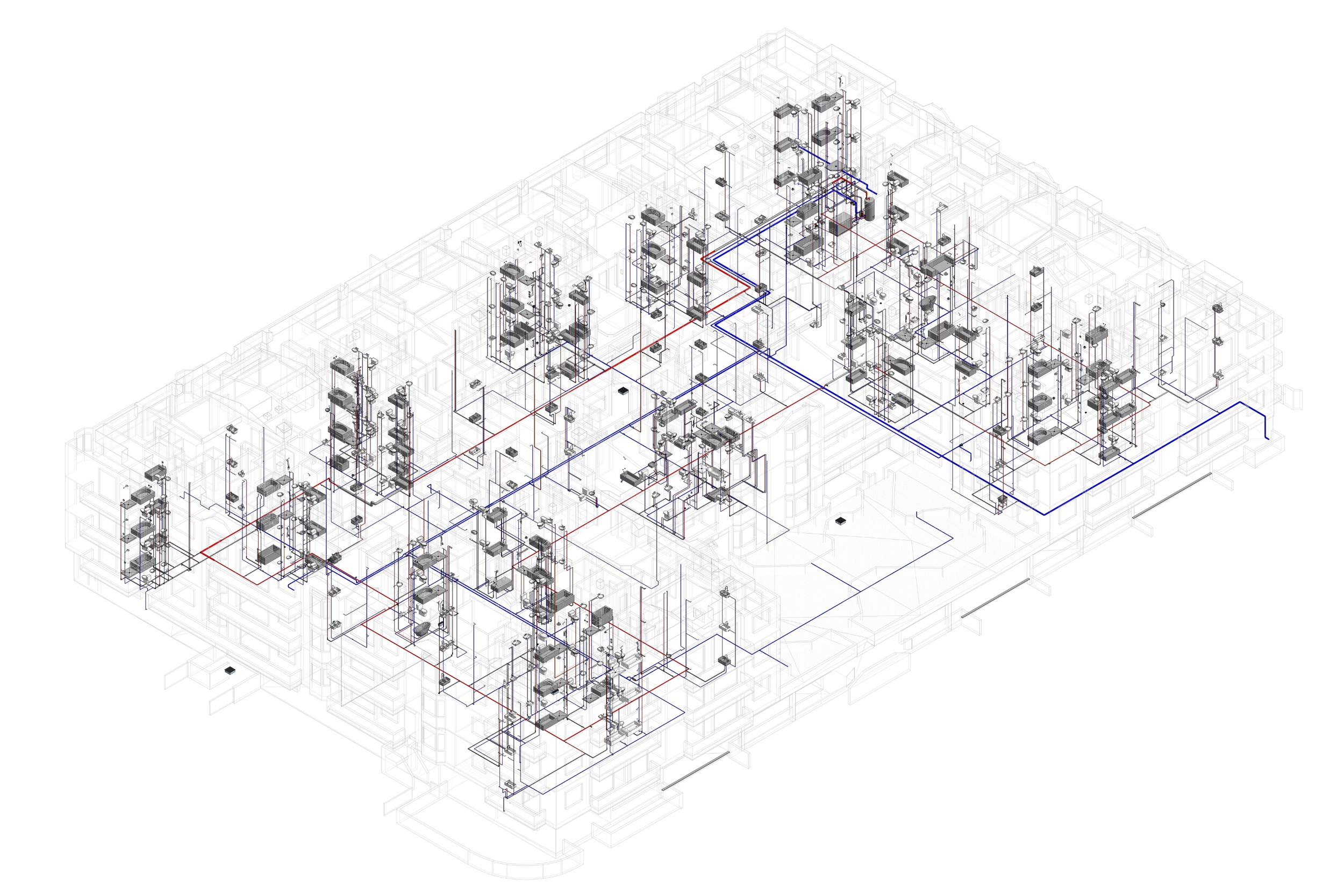
Our BIM Project Examples
BIM Software Programs
Building Information Modeling software is an essential tool in the AEC industry for creating digital representations of a building's physical and functional characteristics. The software enables the creation of 3D models that contain crucial information about every aspect of a building project. For instance, it can include details about materials, dimensions, spatial relationships, and even geographic information.
Here are some popular computer-aided software solutions:
Applications of BIM
1. Architectural Design
It allows them to test designs in a virtual space before construction begins. Architects can explore different layouts, materials, and lighting conditions to create the best possible outcome using the most relevant information.
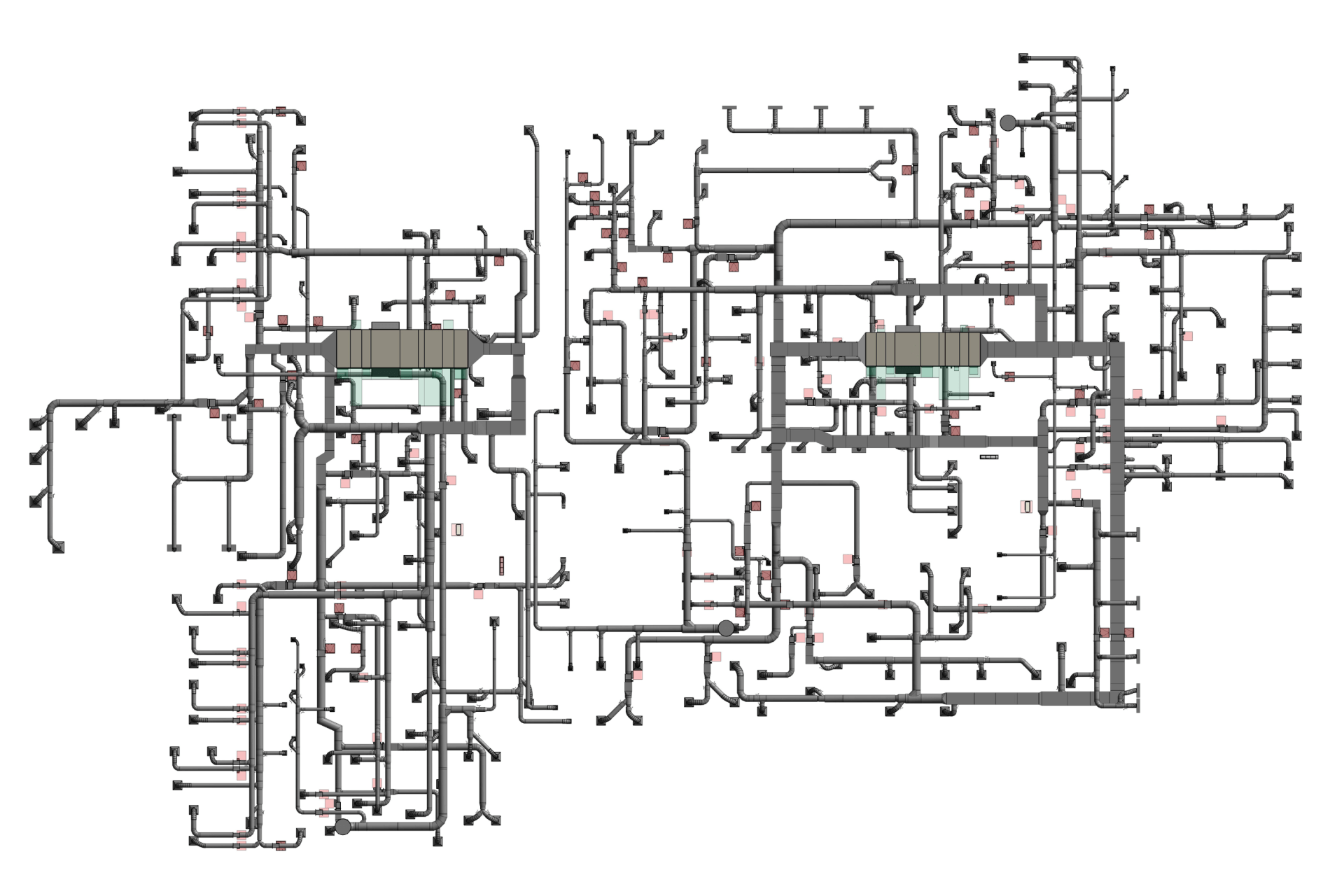
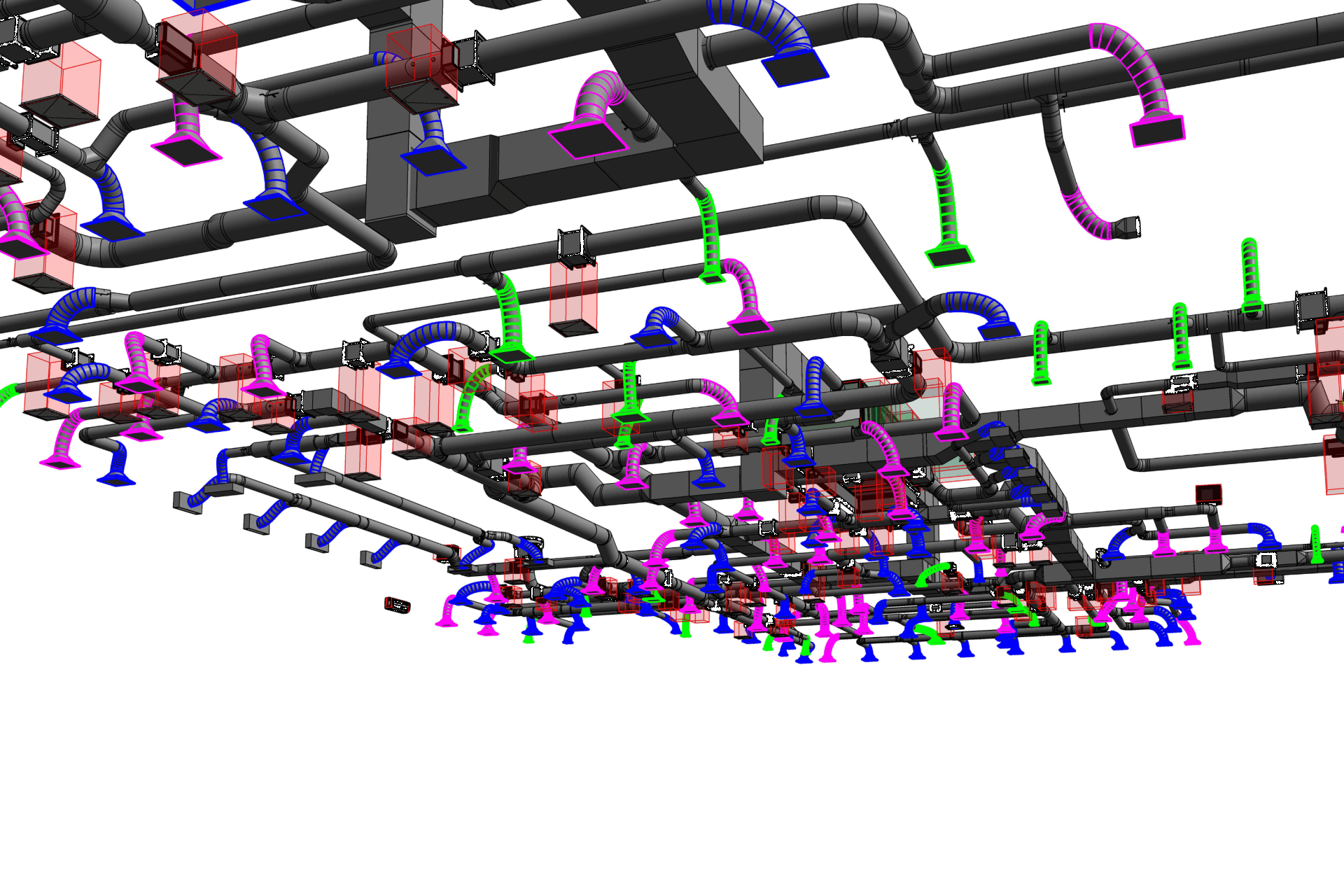
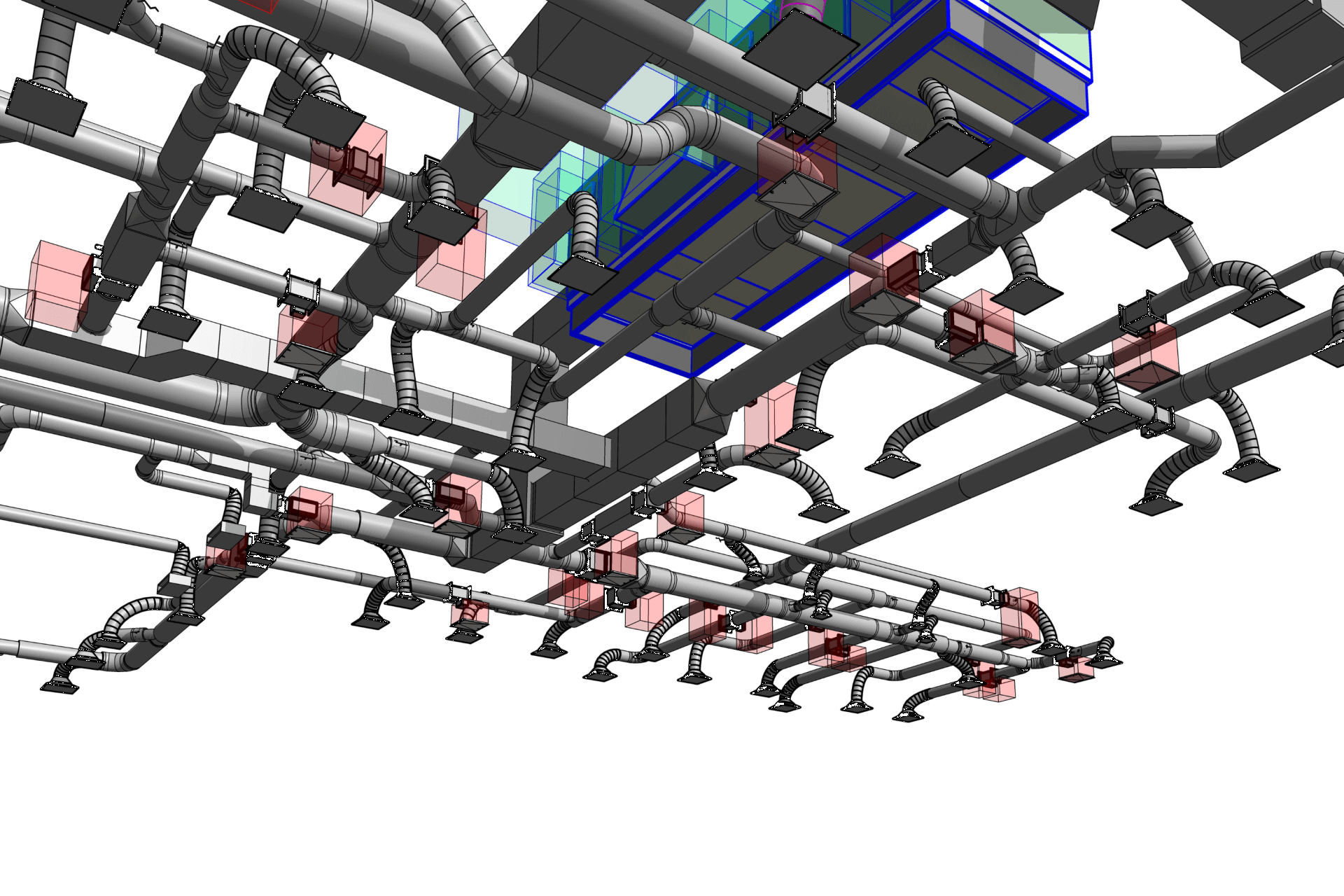
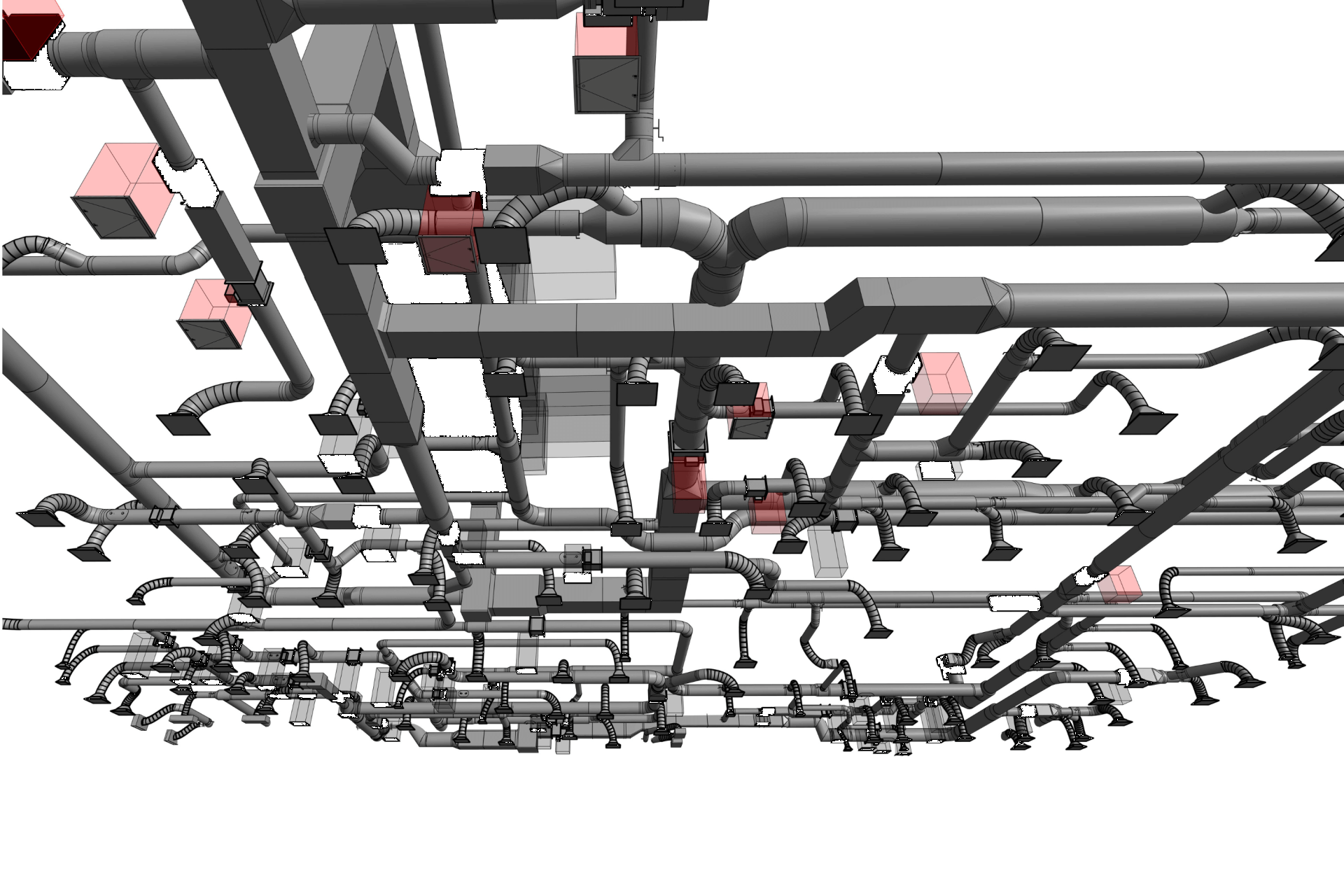
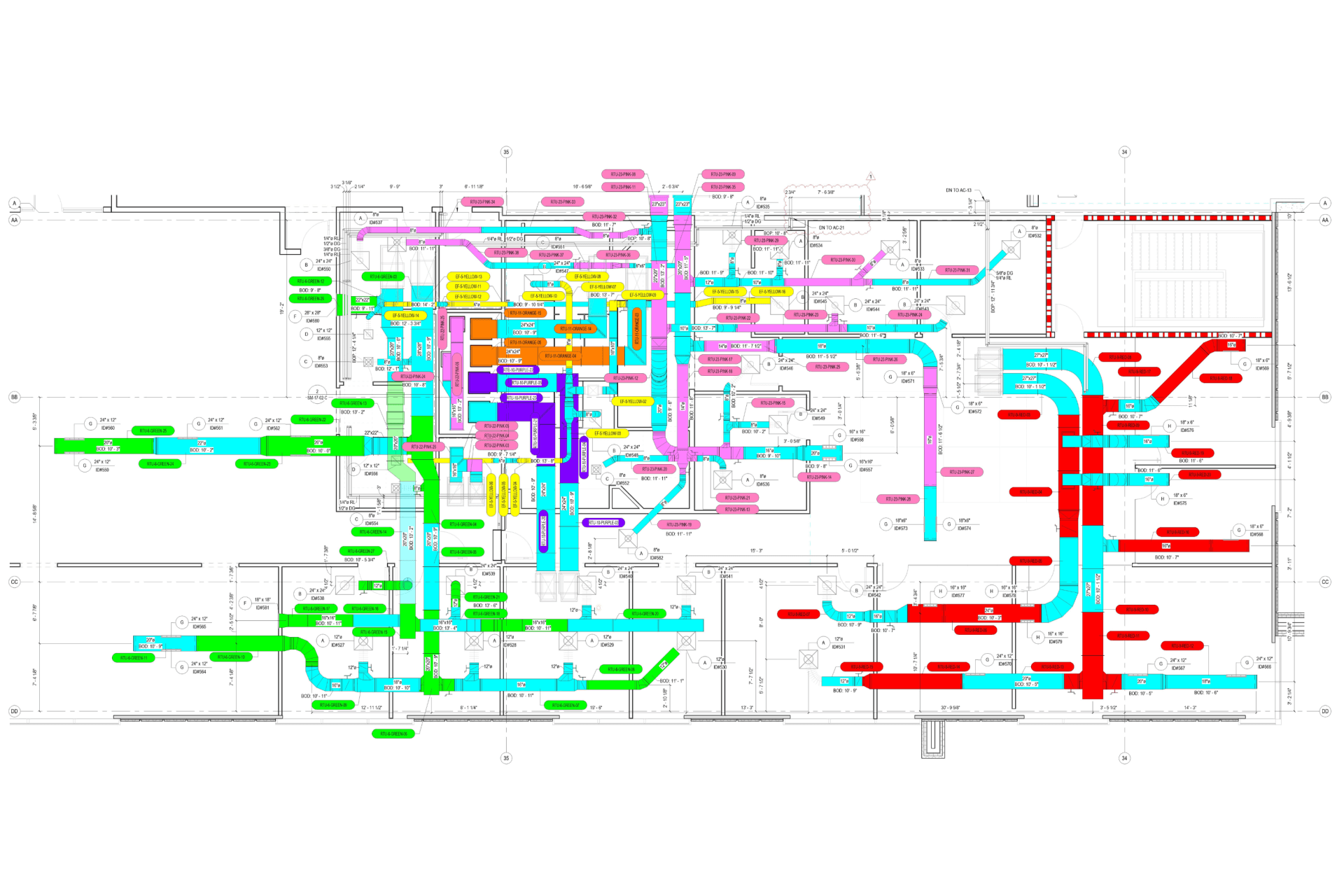
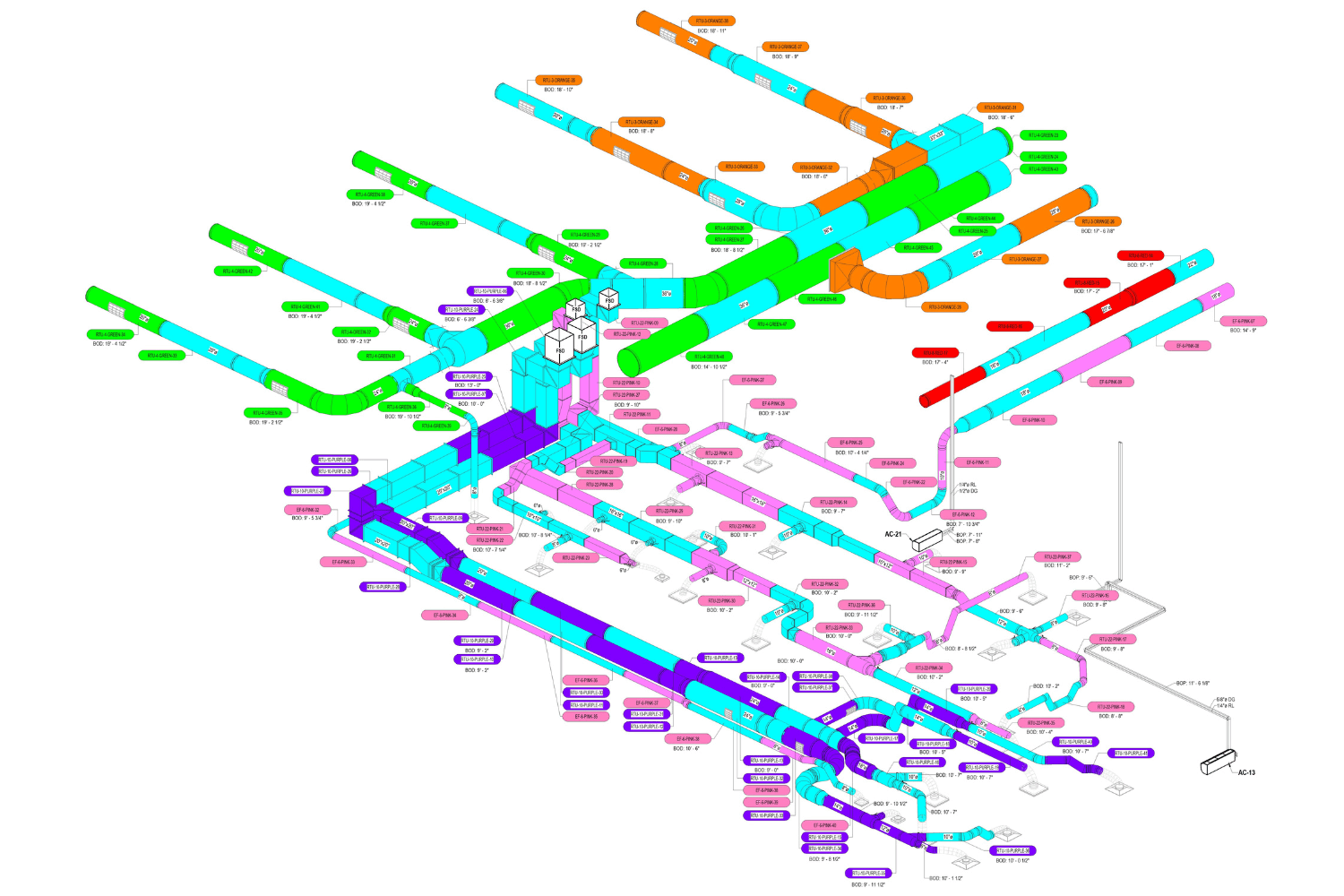
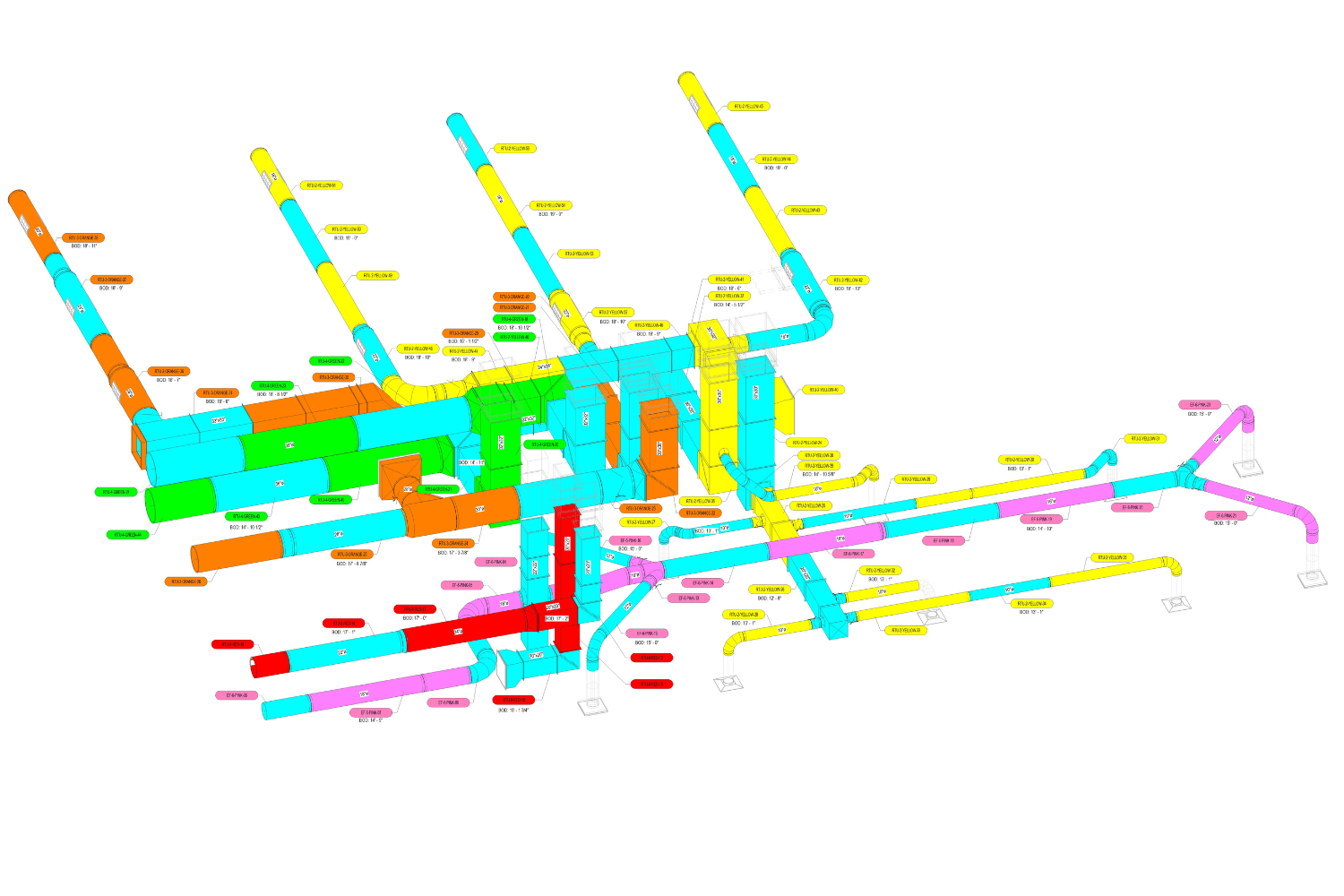
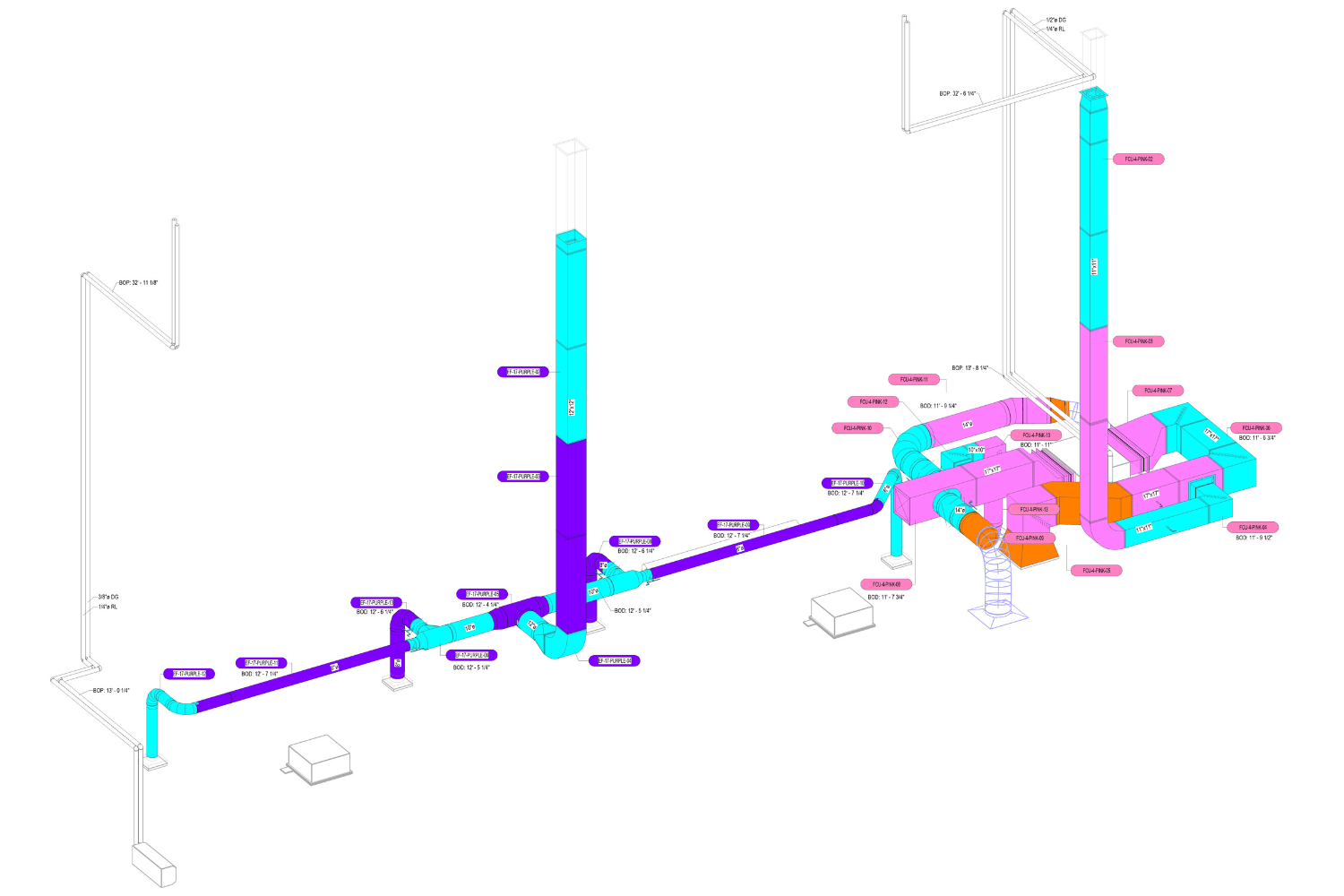
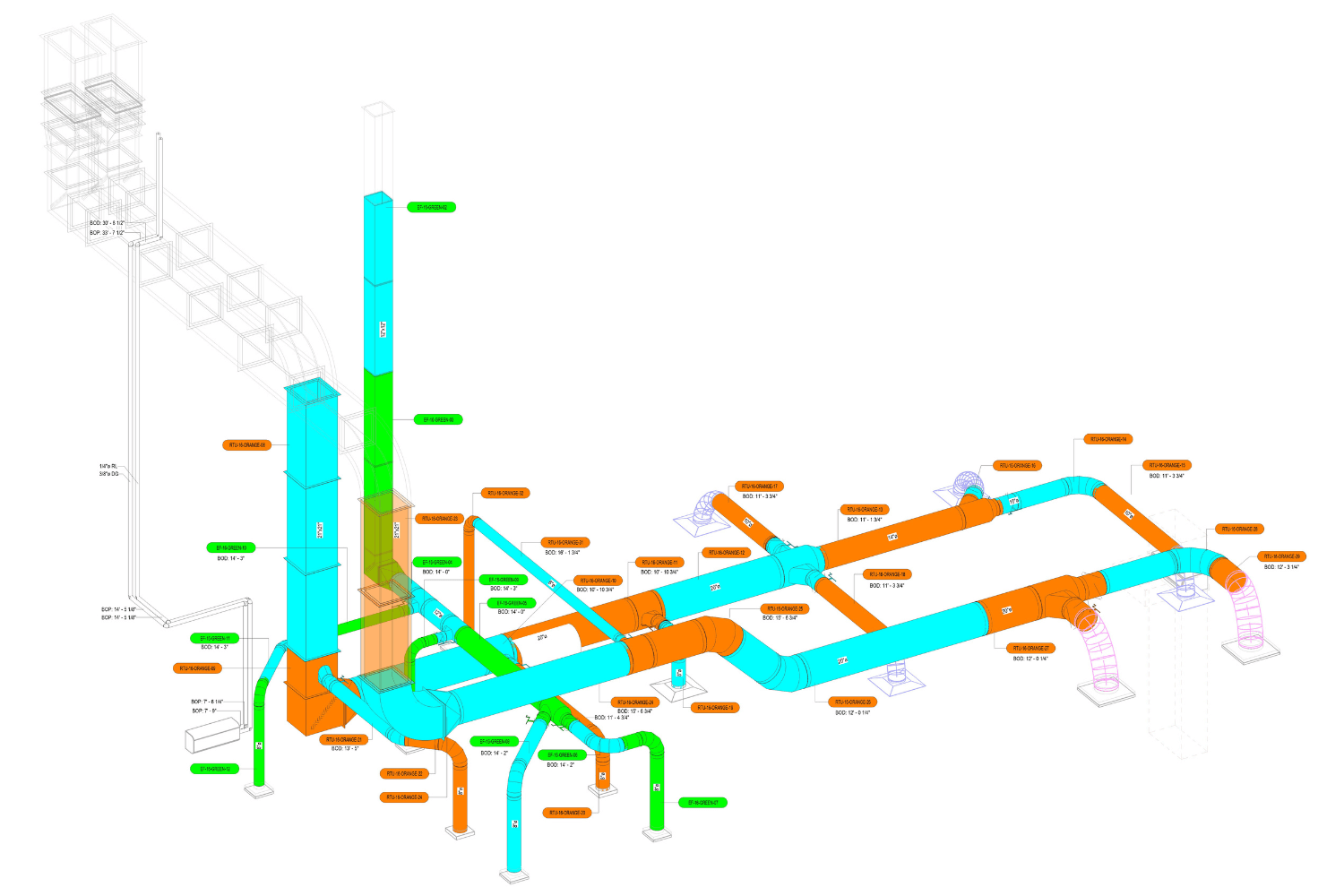
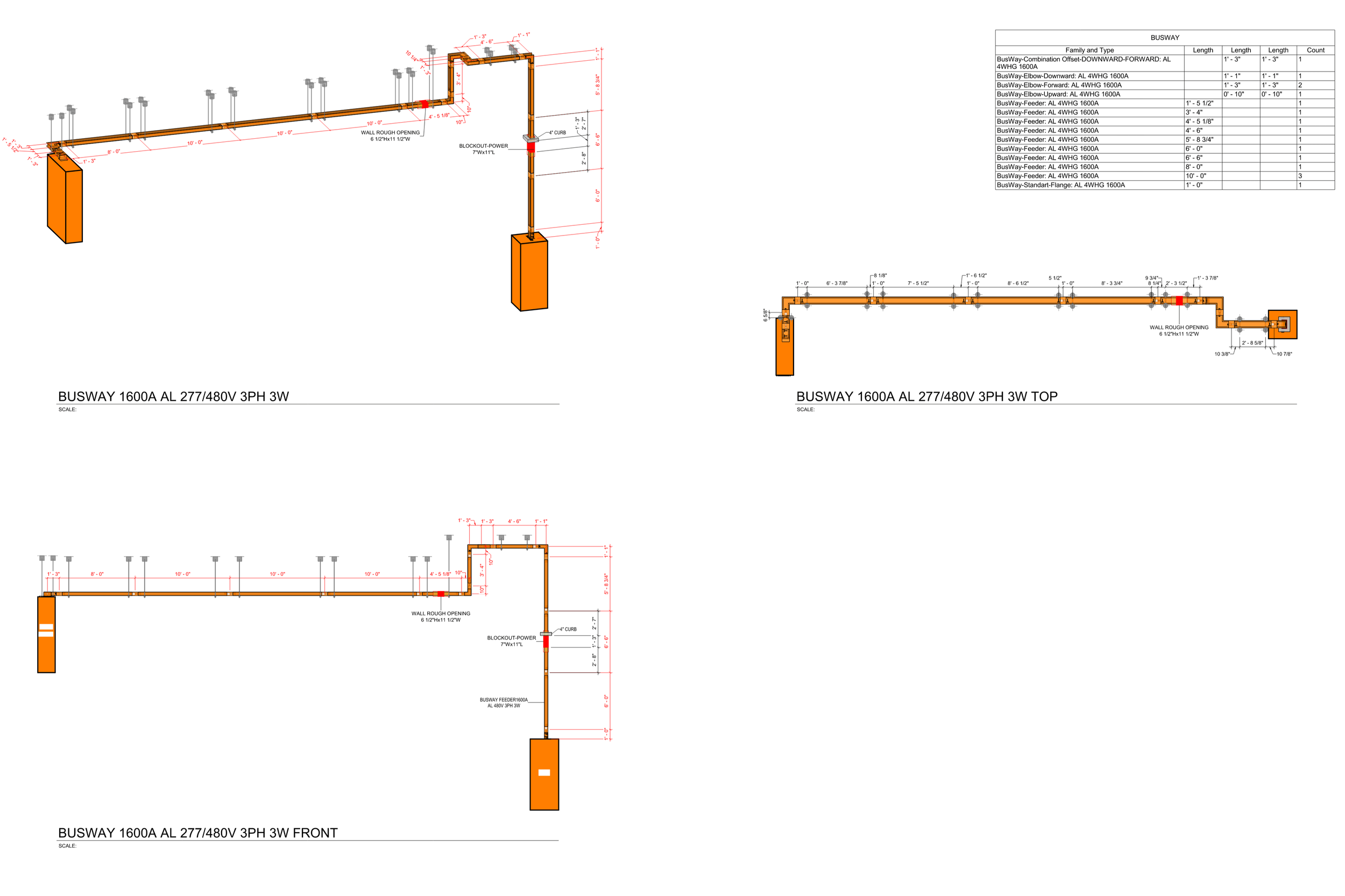
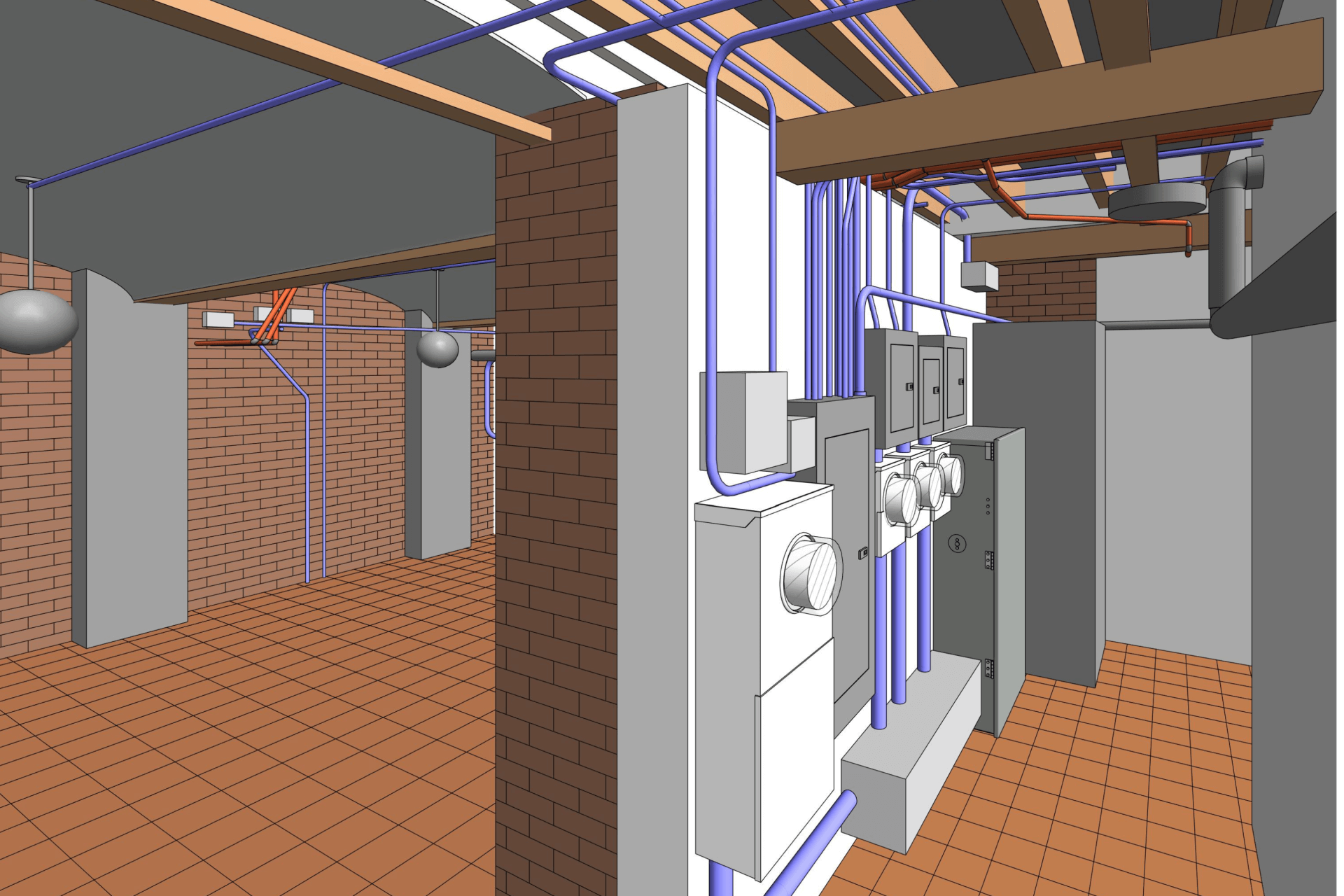
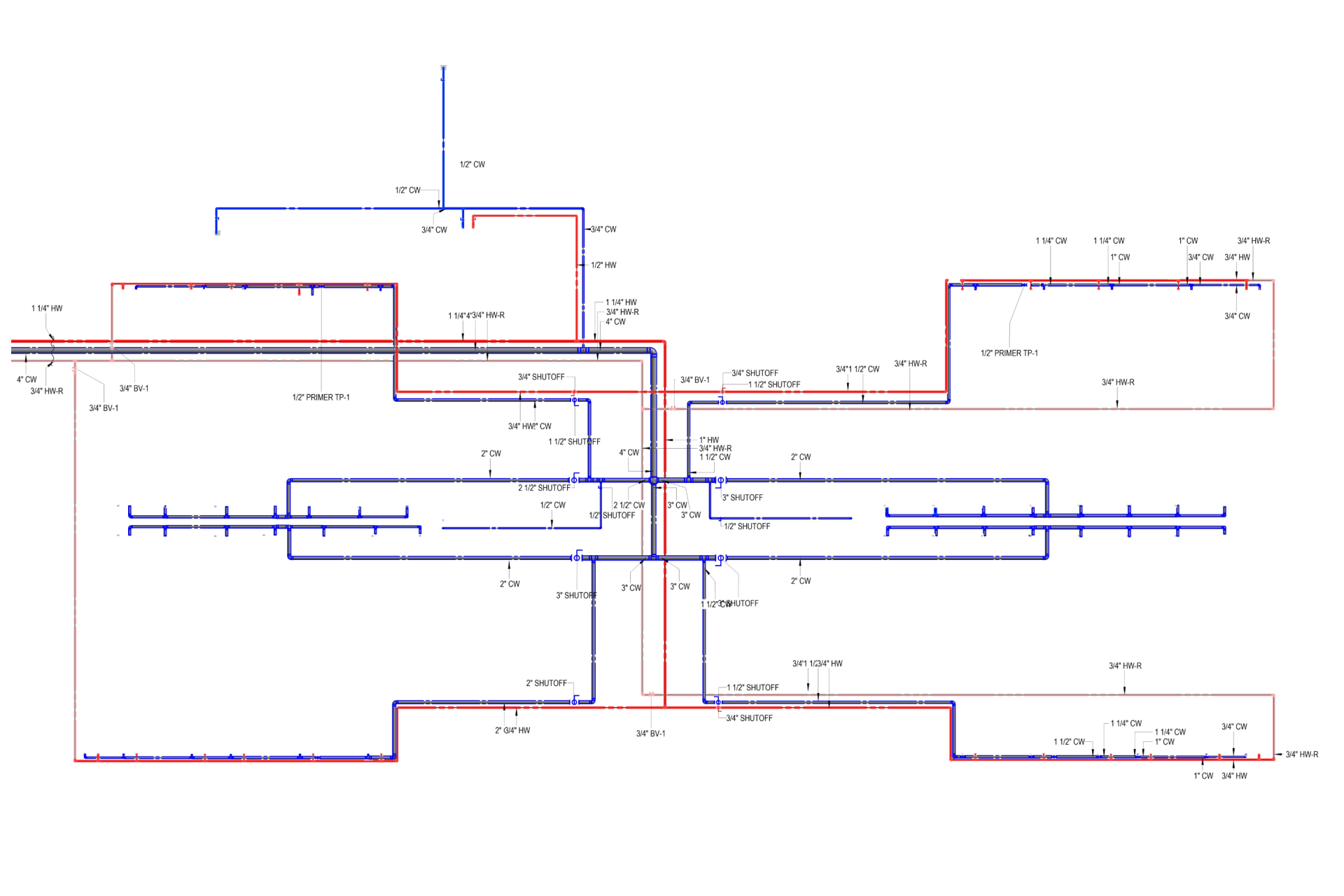
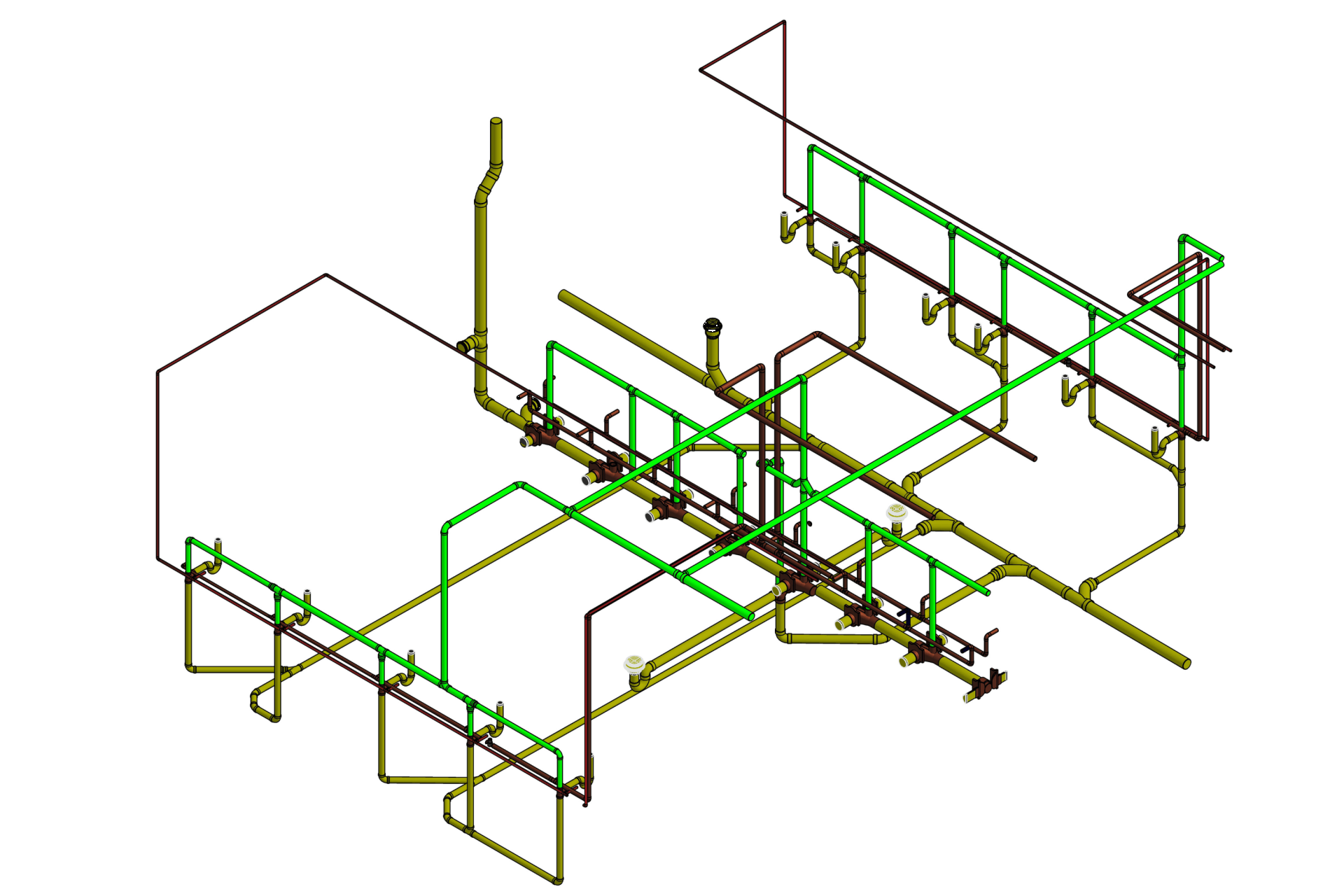
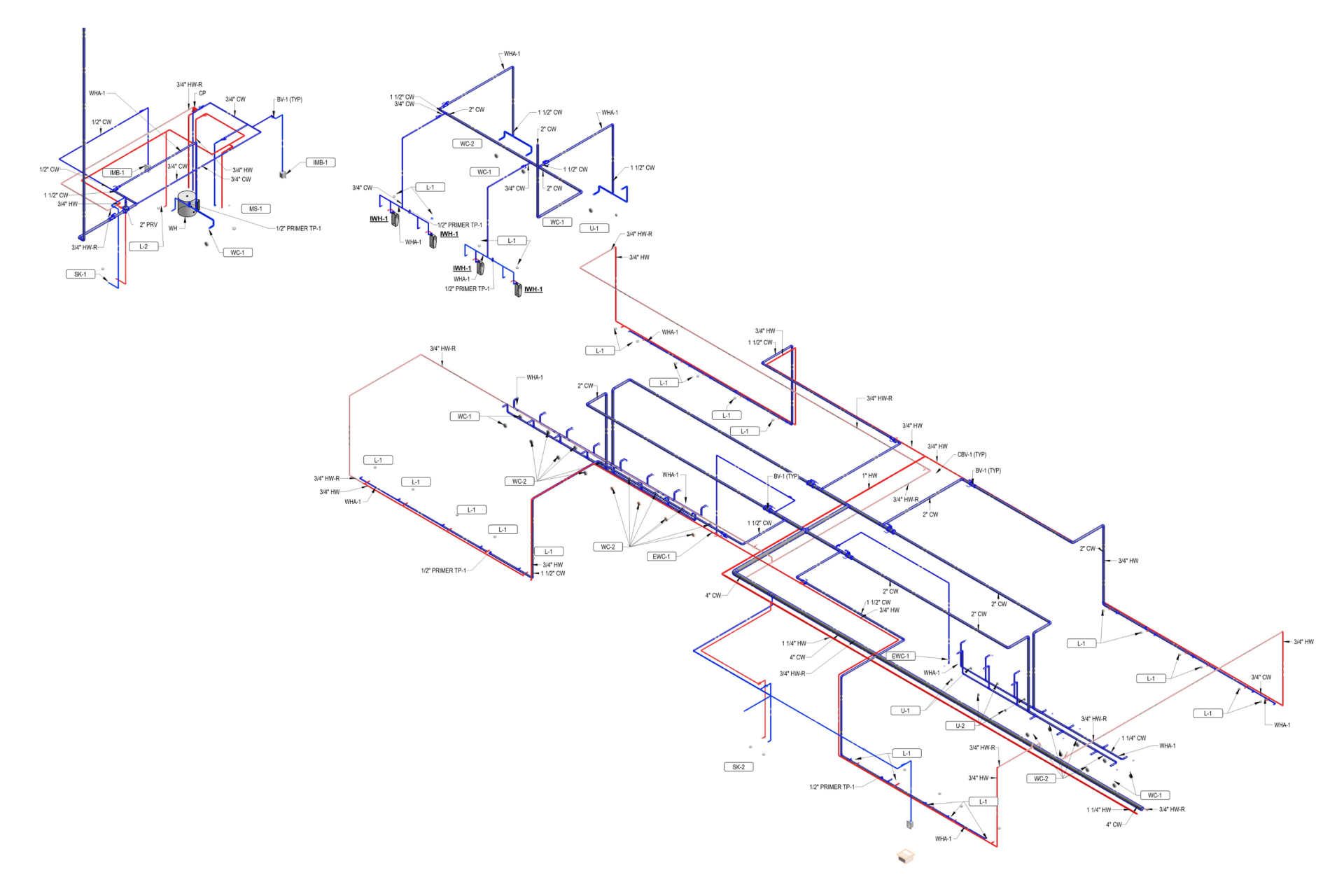
2. MEP Systems
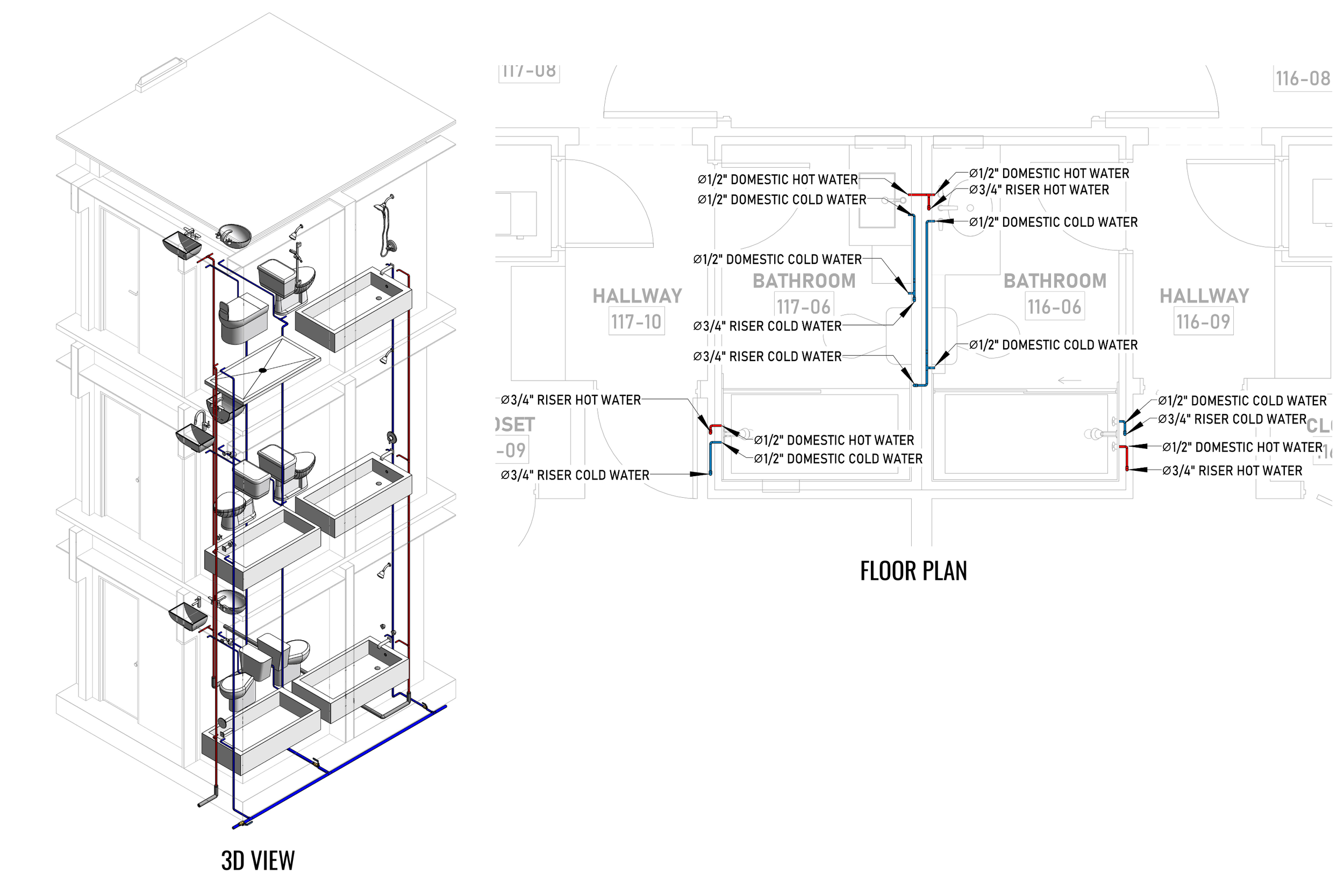
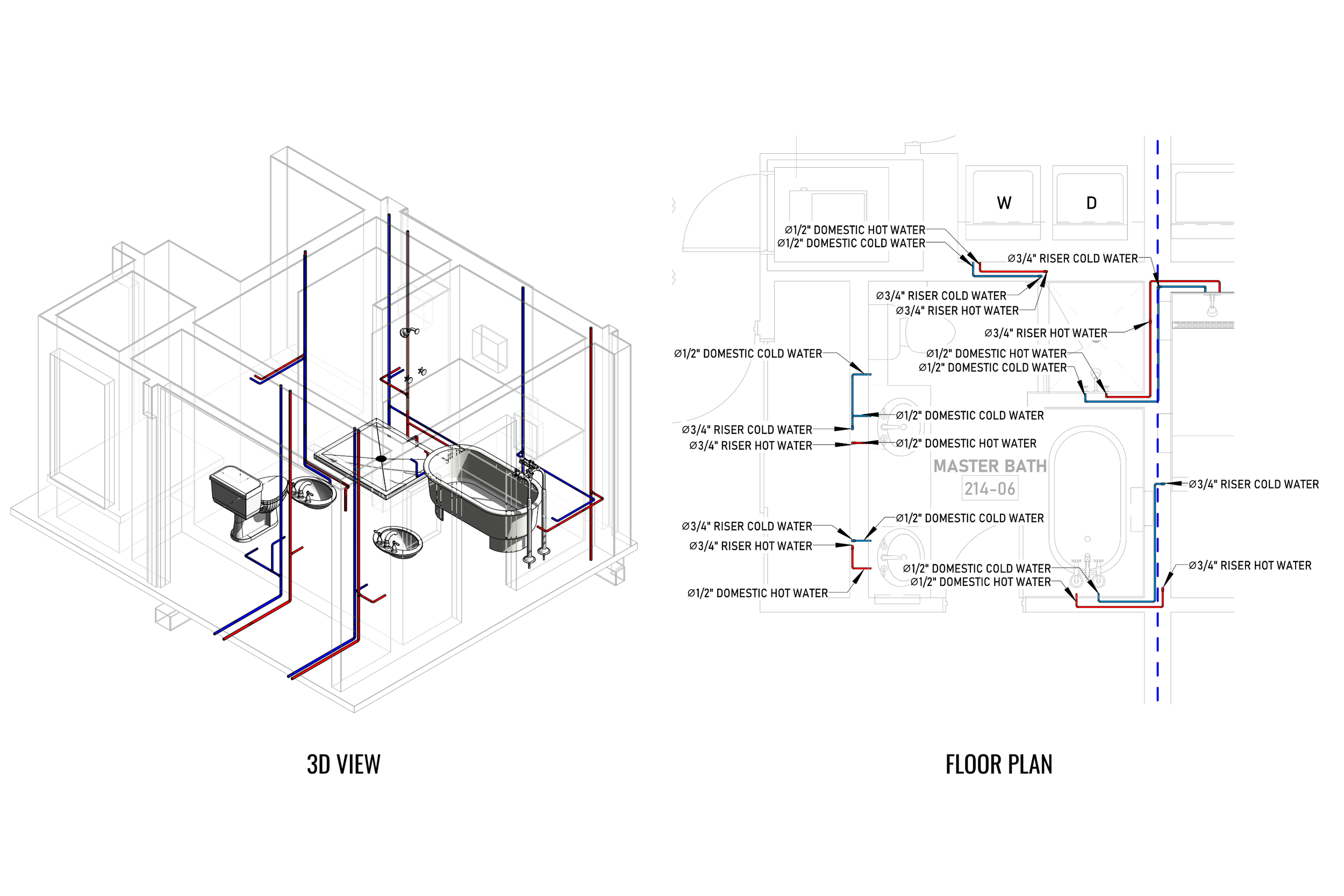
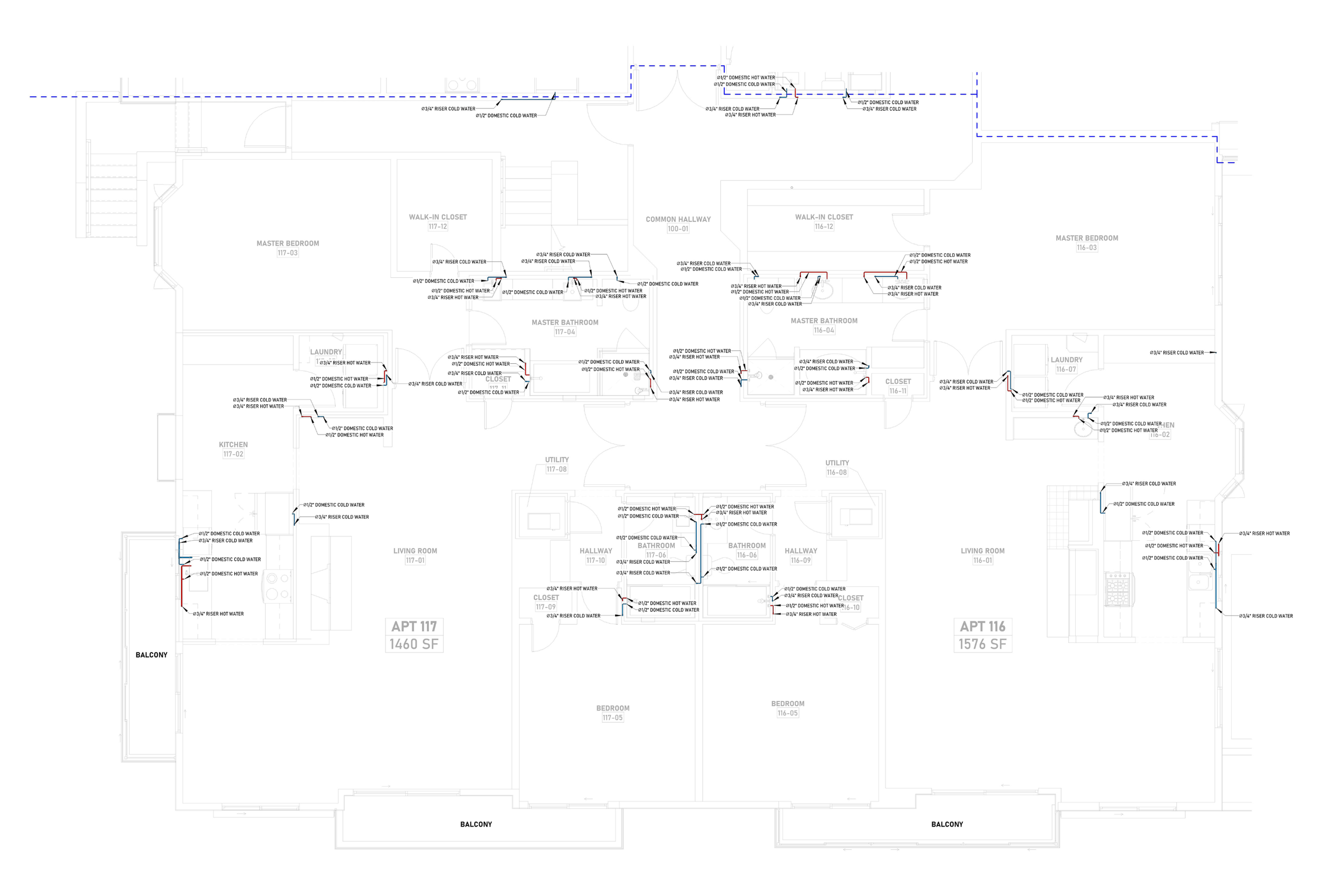
Ensures efficient placement of mechanical, electrical, and plumbing (MEP) systems through accurate production information. Engineers can plan routes for pipes, wires, and ducts in 3D, ensuring everything fits perfectly.
3. Construction Planning
BIM keeps construction organized and efficient. It integrates schedules, materials, and labor needs into a single model. Contractors can plan each stage of the project with precision, reducing delays, cutting costs, and making the construction site more sustainable.
4. Facility Management
Building managers use it to track maintenance schedules, repairs, and upgrades. For instance, if a building system needs fixing, managers can locate it in the BIM model and access all relevant details and asset information, like installation dates or warranty information.
BIM definition lies in INFORMATION and should improve the construction operations building information exchange. All the data can be used in any CAD software. The main goal is building information management and coordination between the parties and any 3D CAD program will do the trick as long as everyone agrees on a specific software. The BIM environment has grown tremendously and if you're ready to embrace it - we're here.