What is an As-Built Plan
Ever wondered how construction projects ensure accuracy and precision in their final built structures? The answer lies in as-built plans. These drawings serve as a crucial documentation tool, providing an accurate representation of the completed project.
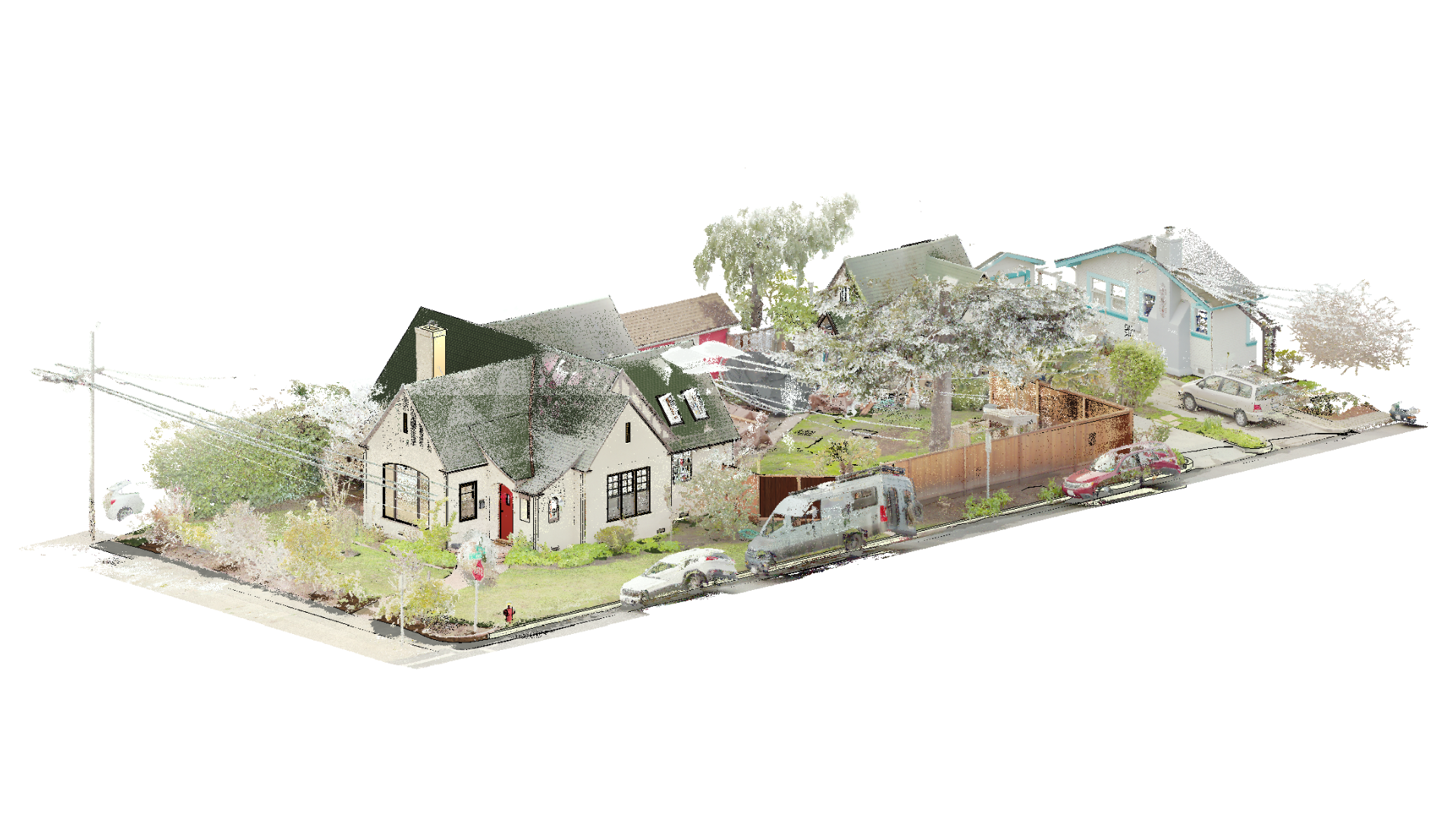
As-built plans are created after construction is finished, capturing any changes or modifications made during the building process and help identify discrepancies between the original designs and the actual construction. They act as a blueprint that reflects the actual state of the structure, including measurements, materials used, and spatial relationships.
Importance of As-Built Plans in Construction
Ensuring Accuracy and Compliance
One key purpose of as-built plans is to document any modifications or deviations from the original design. During construction, unforeseen circumstances may arise that require adjustments to be made. For example, if an architect realizes that a particular wall needs to be moved slightly to accommodate plumbing lines, this change would be reflected in the as-built plan. These modifications are essential for ensuring accuracy and compliance with building codes and regulations.
By comparing as-built plans with the original design documents, project stakeholders can identify any discrepancies or errors that may have occurred during construction. This helps ensure that everything is built according to specifications and allows for timely corrections before completion. For instance, if an electrical outlet was mistakenly placed in the wrong location during construction, it can be rectified by referring to the as-built plan.
.
2. Facilitating Future Maintenance and Repairs
As-built plan records provide valuable information about the location of utility lines, electrical systems, plumbing networks, structural components, and more. When issues arise or repairs need to be made in the future, having accurate as-built plans can significantly streamline the process. Builders can quickly identify where specific elements are located within a structure, saving time and minimizing disruptions. It saves time and reduces potential risks associated with not knowing what lies behind walls or under floors.
3. Enhancing Communication and Collaboration
Effective communication is essential in any construction project, involving multiple stakeholders such as architects, engineers, subcontractors, suppliers, and clients. As-built plans serve as a common reference point for all parties involved. They provide a clear visual representation of how different elements fit together within a structure. This helps prevent misunderstandings or errors due to miscommunication by ensuring that everyone is on the same page regarding design intent.
4. Supporting Documentation for Legal Purposes
In some cases, builders may require supporting documentation for legal purposes related to their projects. As-built plans serve as valuable evidence in disputes or claims involving construction defects or non-compliance with contractual obligations. These detailed records can help establish what was originally agreed upon in terms of design specifications and assist in resolving any conflicts that may arise.
Key Components of As-Built Plans
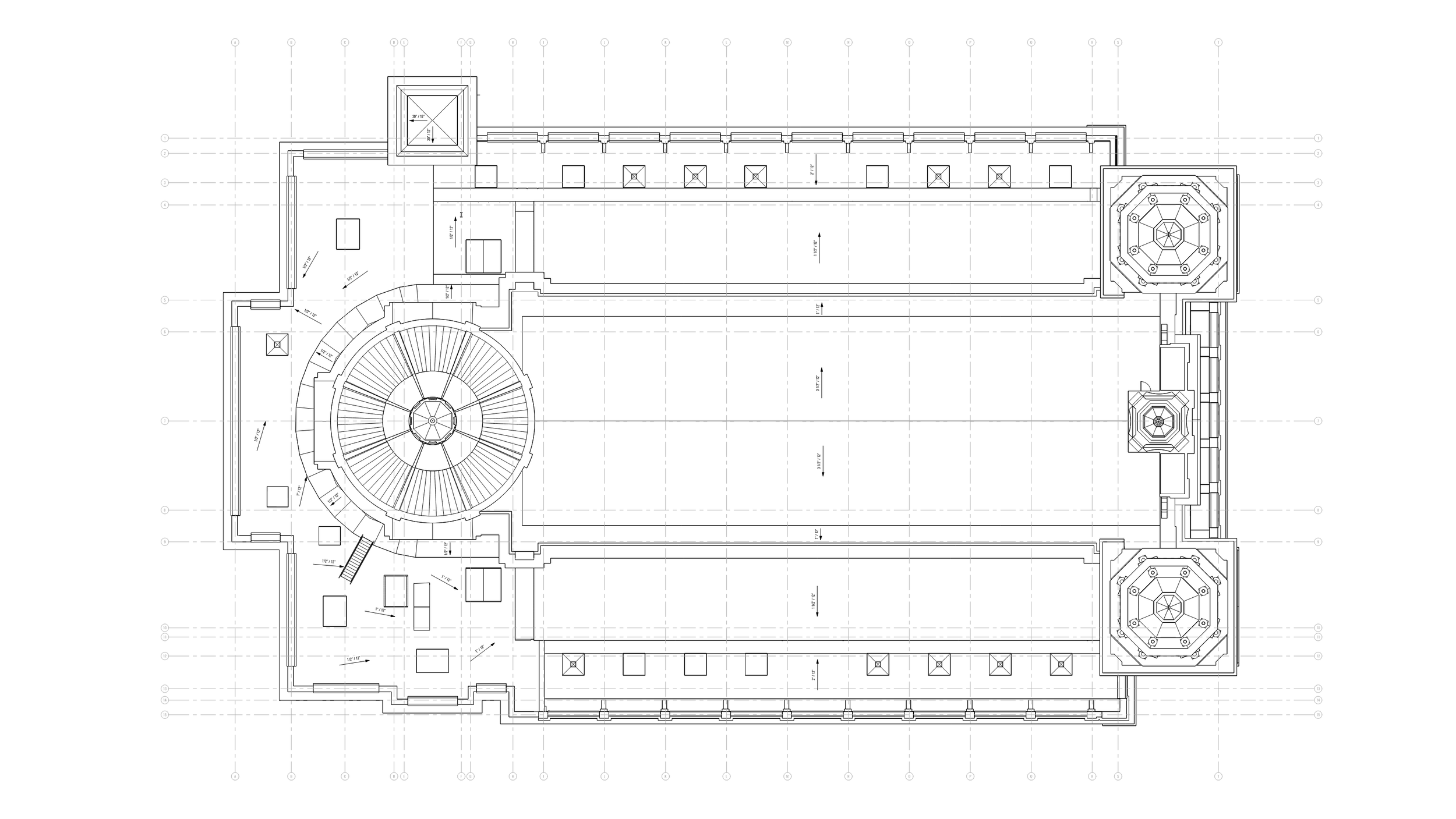
Floor Plans
Floor plans are an integral component of as-built plans. They provide a bird's-eye view of each level within a building, illustrating the layout and arrangement of rooms, corridors, staircases, and other structural elements. Floor plans help architects visualize the spatial organization and flow within a building while also aiding in identifying potential design issues or discrepancies between the original design intent and the constructed reality.
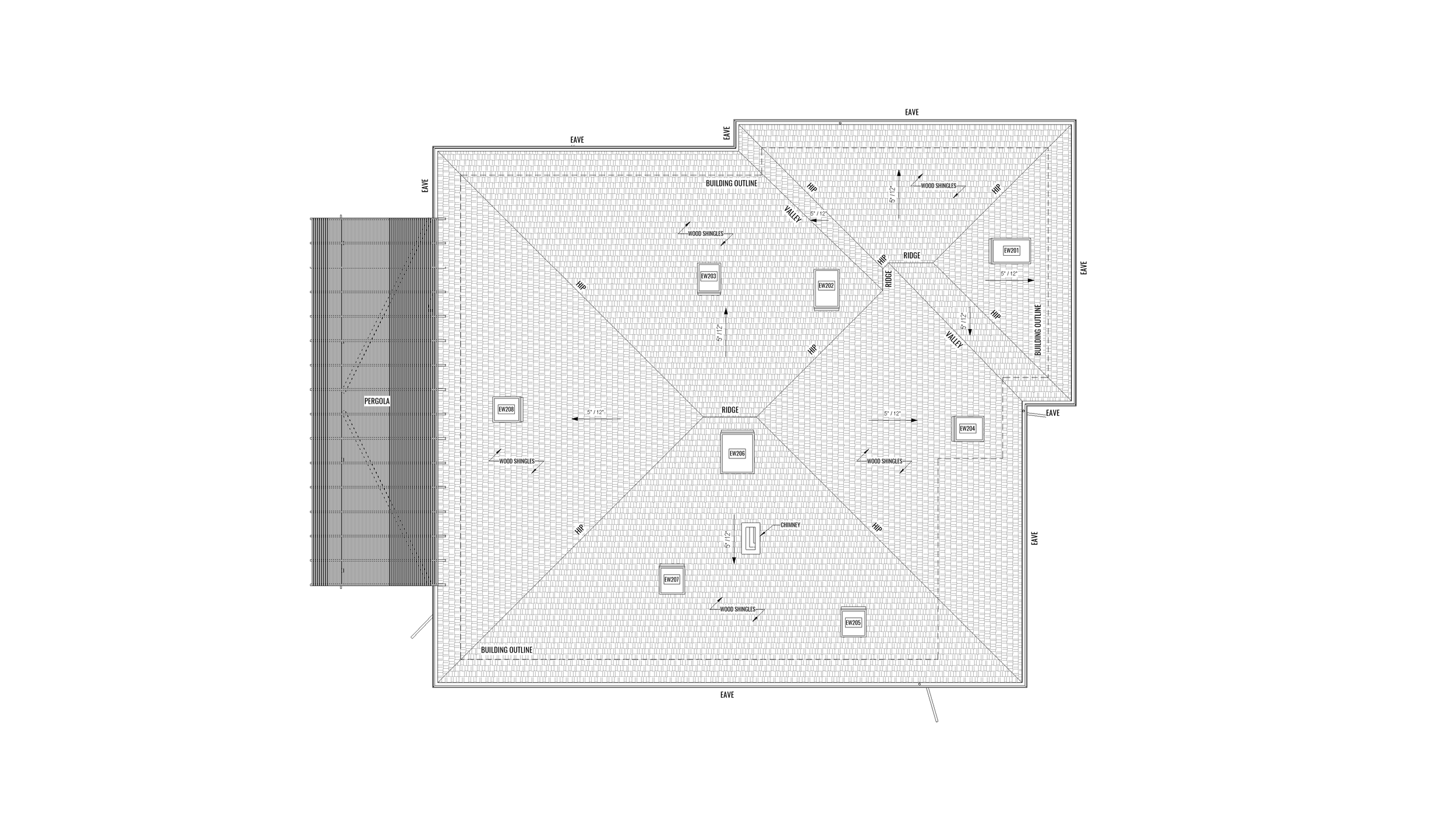
Roof Plan
A roof plan is a detailed, overhead view or diagram that provides a comprehensive representation of the design and structure of a building's roof. This architectural drawing typically includes essential information about the roof's geometry, layout, materials, and various components.
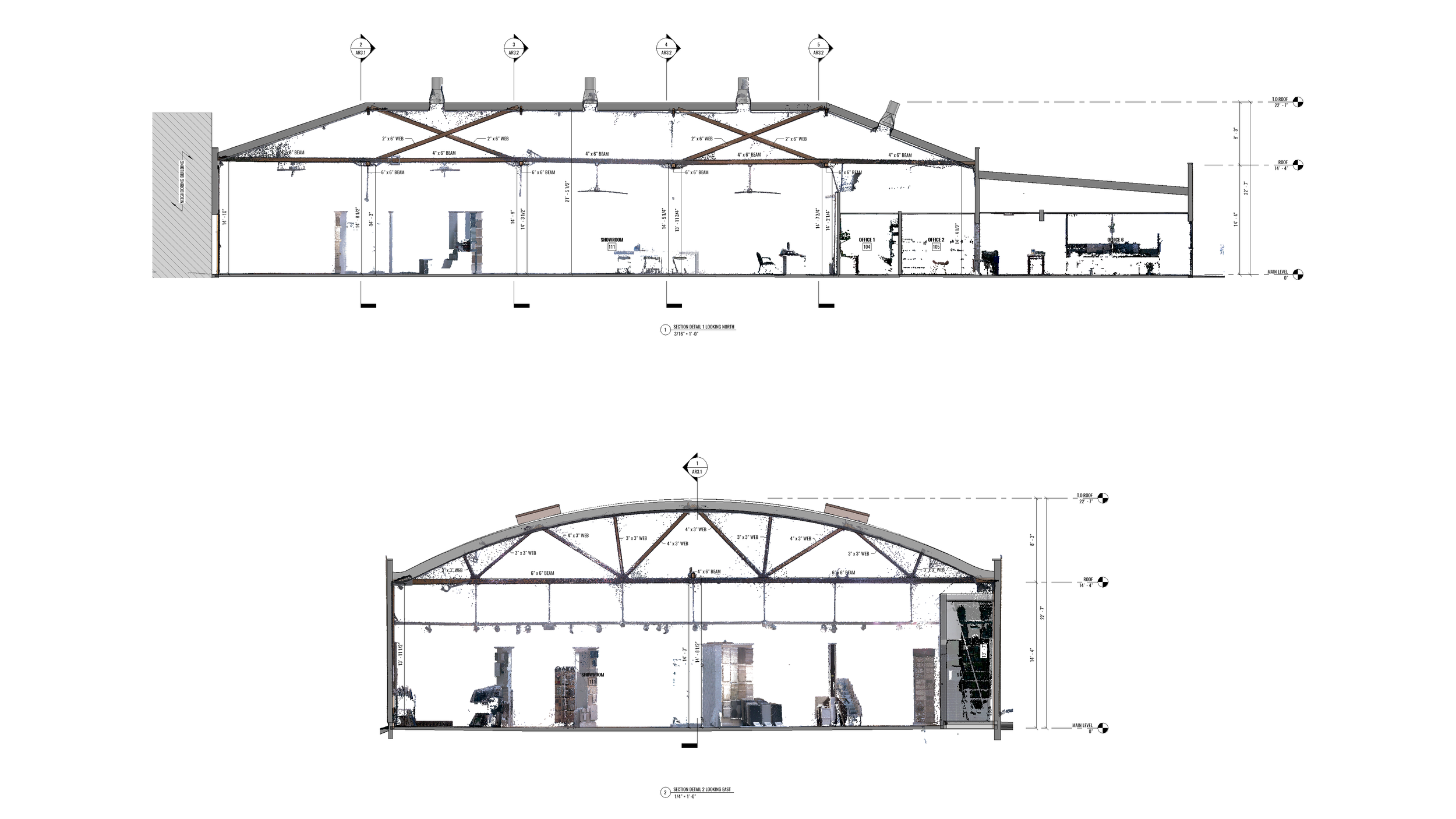
Elevations
Elevations are another critical element found in as-built drawings. These drawings depict the vertical faces or facades of a building from different angles. Elevations showcase important architectural features such as windows, doors, exterior finishes, rooflines, and decorative elements. By including elevations in as-built plans, architects can accurately capture any modifications made during construction that may impact the overall appearance or aesthetic appeal of the structure.
Depending on your needs and goals the As-Builts may also include other plans like site plan, electrical and lighting, framing, and other details. It is aways recommended to discuss the scope of work with your as-built team to make sure that all important elements will be measured and included into your set of plans.
The Creation Process of As-Built Drawings
To accurately depict the built environment, as-built drawings are created through a meticulous process that involves surveying the completed structure and using specialized software. Let's explore the creation process in more detail.
Surveying the Completed Structure
The first step in creating as-built drawings is to conduct a thorough survey of the completed structure. This involves visiting the site and taking detailed measurements of various elements such as walls, floors, windows, doors, and other architectural features. Skilled professionals, such as architects or surveyors, use precision instruments like laser scanners or total stations to ensure accurate measurements.
During this phase, it is crucial to capture all relevant information about the existing conditions of the building or space. This includes any modifications made during construction that may differ from the original design plans. By documenting these changes accurately, as-built drawings provide an up-to-date record of how the structure was actually built.
Accurate Measurements for Depiction
Once all necessary measurements have been taken, they are used to create accurate depictions of the built environment. These depictions typically include floor plans, elevations, sections, and details that showcase different aspects of the structure. By using precise measurements obtained during the surveying process, designers can ensure that their drawings reflect reality.
Specialized Software for Precision
Creating precise as-built drawings requires specialized software that allows designers to translate measurements into digital representations accurately.
Software enables designers to input measured dimensions and create scaled representations of various architectural elements. They can add annotations, labels, and symbols to provide additional information about the building's features. With the help of this software, as-built drawings can be easily modified or updated as needed.